PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway: A Therapeutic Target in CD30+ Large Cell Lymphomas
- PMID: 35884893
- PMCID: PMC9313053
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10071587
PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway: A Therapeutic Target in CD30+ Large Cell Lymphomas
Abstract
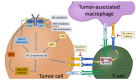
The programmed death-ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2, reside on tumor cells and can bind with programmed death-1 protein (PD-1) on T-cells, resulting in tumor immune escape. PD-1 ligands are highly expressed in some CD30+ large cell lymphomas, including classic Hodgkin lymphoma (CHL), primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBL), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (EBV+ DLBCL), and anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL). The genetic alteration of the chromosome 9p24.1 locus, the location of PD-L1, PD-L2, and JAK2 are the main mechanisms leading to PD-L1 and PD-L2 overexpression and are frequently observed in these CD30+ large cell lymphomas. The JAK/STAT pathway is also commonly constitutively activated in these lymphomas, further contributing to the upregulated expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2. Other mechanisms underlying the overexpression of PD-L1 and PD-L2 in some cases include EBV infection and the activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. These cellular and molecular mechanisms provide a scientific rationale for PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in treating patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) disease and, possibly, in newly diagnosed patients. Given the high efficacy of PD-1 inhibitors in patients with R/R CHL and PMBL, these agents have become a standard treatment in these patient subgroups. Preliminary studies of PD-1 inhibitors in patients with R/R EBV+ DLBCL and R/R ALCL have also shown promising results. Future directions for these patients will likely include PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in combination with other therapeutic agents, such as brentuximab or traditional chemotherapy regimens.
Keywords: CD30; PD-1; PD-L1; large cell lymphoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Programmed Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Expression in Lymphomas: State of the Art.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 11;25(12):6447. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126447. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway and Its Blockade in Patients with Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma and Non-Hodgkin Large-Cell Lymphomas.Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2020 Aug;15(4):372-381. doi: 10.1007/s11899-020-00589-y. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2020. PMID: 32394185 Review.
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitors in malignant lymphoma: Advances and perspectives.Chin J Cancer Res. 2020 Jun;32(3):303-318. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2020.03.03. Chin J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32694896 Free PMC article.
-
Frequent structural variations involving programmed death ligands in Epstein-Barr virus-associated lymphomas.Leukemia. 2019 Jul;33(7):1687-1699. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0380-5. Epub 2019 Jan 25. Leukemia. 2019. PMID: 30683910 Free PMC article.
-
Programmed cell death ligand 1 expression in aggressive pediatric non-Hodgkin lymphomas: frequency, genetic mechanisms, and clinical significance.Haematologica. 2022 Aug 1;107(8):1880-1890. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2021.280342. Haematologica. 2022. PMID: 35081690 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
PD-L1 expression in pancreaticobiliary adenosquamous carcinoma: a single-institution case series.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024 Apr 30;15(2):768-779. doi: 10.21037/jgo-24-9. Epub 2024 Apr 25. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38756636 Free PMC article.
-
Drug resistance mechanism and reversal strategy in lung cancer immunotherapy.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Sep 19;14:1230824. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1230824. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37795038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RBM30 recruits DOT1L to activate STAT1 transcription and drive immune evasion in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncogene. 2025 Aug 29. doi: 10.1038/s41388-025-03550-6. Online ahead of print. Oncogene. 2025. PMID: 40883414
-
Sequential immunotherapy and targeted therapy for metastatic BRAF V600 mutated melanoma: 4-year survival and biomarkers evaluation from the phase II SECOMBIT trial.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 2;15(1):146. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-44475-6. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38167503 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Programmed Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) Expression in Lymphomas: State of the Art.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 11;25(12):6447. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126447. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928153 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

