Optimizing Therapies in Heart Failure: The Role of Potassium Binders
- PMID: 35885026
- PMCID: PMC9313061
- DOI: 10.3390/biomedicines10071721
Optimizing Therapies in Heart Failure: The Role of Potassium Binders
Abstract
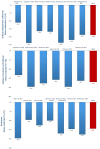
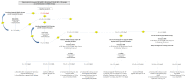
Heart failure (HF) is a worrisome cardiac pandemic with a negative prognostic impact on the overall survival of individuals. International guidelines recommend up-titration of standardized therapies in order to reduce symptoms, hospitalization rates, and cardiac death. Hyperkalemia (HK) has been identified in 3-18% of HF patients from randomized controlled trials and over 25% of HF patients in the "real world" setting. Pharmacological treatments and/or cardio-renal syndrome, as well as chronic kidney disease may be responsible for HK in HF patients. These conditions can prevent the upgrade of pharmacological treatments, thus, negatively impacting on the overall prognosis of patients. Potassium binders may be the best option in patients with HK in order to reduce serum concentrations of K+ and to promote correct upgrades of therapies. In addition to the well-established use of sodium polystyrene sulfonate (SPS), two novel drugs have been recently introduced: sodium zirconium cyclosilicate (SZC) and patiromer. SZC and patiromer are gaining a central role for the treatment of chronic HK. SZC has been shown to reduce K+ levels within 48 h, with guaranteed maintenance of normokalemia for up to12 months. Patiromer has resulted in a statistically significant decrease in serum potassium for up to 52 weeks. Therefore, long-term results seemed to positively promote the implementation of these compounds in clinical practice due to their low rate side effects. The aim of this narrative review is to delineate the impact of new potassium binders in the treatment of patients with HF by providing a critical reappraisal for daily application of novel therapies for hyperkalemia in the HF setting.
Keywords: heart failure; management; patiromer; prognosis; sodium zirconium cyclosilicate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- McDonagh T.A., Metra M., Adamo M., Gardner R.S., Baumbach A., Böhm M., Burri H., Butler J., Čelutkienė J., Chioncel O., et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: Developed by the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). With the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2022;24:4–131. - PubMed
-
- Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation (HOPE) Study Investigators Effects of ramipril on cardiovascular and microvascular outcomes in people with diabetes mellitus: Results of the HOPE study and MICRO-HOPE substudy. Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation Study Investigators. Lancet. 2000;355:253–259. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(99)12323-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yusuf S., Pitt B., Davis C.E., Hood W.B., Cohn J.N. Effect of enalapril on survival in patients with reduced left ventricular ejection fractions and congestive heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991;325:293–302. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

