Myelodysplastic Syndrome: Diagnosis and Screening
- PMID: 35885487
- PMCID: PMC9319204
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12071581
Myelodysplastic Syndrome: Diagnosis and Screening
Abstract
Myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) are heterogeneous groups of clonal myeloid disorders characterized by unexplained persistent peripheral blood (PB) cytopenia(s) of one or more of the hematopoietic lineages, or bone marrow (BM) morphologic dysplasia in hematopoietic cells, recurrent genetic abnormalities, and an increased risk of progression to acute myeloid leukemia (AML). In the past several years, diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic approaches have substantially improved with the development of Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) diagnostic testing and new medications. However, there is no single diagnostic parameter specific for MDS, and correlations with clinical information, and laboratory test findings are needed to reach the diagnosis.
Keywords: cytogenetics; myelodysplastic syndromes; next generation sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
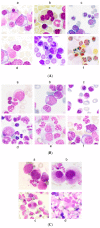
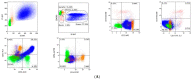


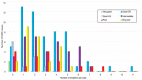

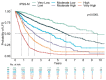

References
-
- Olcay L., Yetgin S. Disorders Mimicking Myelodysplastic Syndrome and Difficulties in Its Diagnosis. IntechOpen; London, UK: 2016. - DOI
-
- Arber D.A., Orazi A., Hasserjian R., Thiele J., Borowitz M.J., Le Beau M.M., Bloomfield C.D., Cazzola M., Vardiman J.W. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 2016;127:2391–2405. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-03-643544. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

