MiRNAs in Lung Cancer: Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Potential
- PMID: 35885514
- PMCID: PMC9322918
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12071610
MiRNAs in Lung Cancer: Diagnostic, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Potential
Abstract
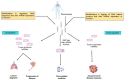
Lung cancer is the dominant emerging factor in cancer-related mortality around the globe. Therapeutic interventions for lung cancer are not up to par, mainly due to reoccurrence/relapse, chemoresistance, and late diagnosis. People are currently interested in miRNAs, which are small double-stranded (20-24 ribonucleotides) structures that regulate molecular targets (tumor suppressors, oncogenes) involved in tumorigeneses such as cell proliferation, apoptosis, metastasis, and angiogenesis via post-transcriptional regulation of mRNA. Many studies suggest the emerging role of miRNAs in lung cancer diagnostics, prognostics, and therapeutics. Therefore, it is necessary to intensely explore the miRNOME expression of lung tumors and the development of anti-cancer strategies. The current review focuses on the therapeutic, diagnostic, and prognostic potential of numerous miRNAs in lung cancer.
Keywords: diagnostics; lung cancer; miRNA; therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA in lung cancer: role, mechanisms, pathways and therapeutic relevance.Mol Aspects Med. 2019 Dec;70:3-20. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2018.07.003. Epub 2018 Aug 18. Mol Aspects Med. 2019. PMID: 30102929 Review.
-
MicroRNAs and lung cancer: new oncogenes and tumor suppressors, new prognostic factors and potential therapeutic targets.Curr Med Chem. 2009;16(9):1047-61. doi: 10.2174/092986709787581833. Curr Med Chem. 2009. PMID: 19275611 Review.
-
miRNA and cancer; computational and experimental approaches.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014;15(5):429. doi: 10.2174/138920101505140828161335. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25189575
-
microRNAs as oncogenes and tumor suppressors.Dev Biol. 2007 Feb 1;302(1):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.08.028. Epub 2006 Aug 16. Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 16989803 Review.
-
The Role of Dysregulated MicroRNA Expression in Lung Cancer.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016;911:1-8. doi: 10.1007/5584_2016_219. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016. PMID: 26987328 Review.
Cited by
-
Current Evidence Supporting the Role of miRNA as a Biomarker for Lung Cancer Diagnosis Through Exhaled Breath Condensate Collection: A Narrative Review.Life (Basel). 2025 Apr 22;15(5):683. doi: 10.3390/life15050683. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on the mechanism of exosome-mediated virus infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jun 26;14:1418168. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1418168. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38988816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Small RNA Landscape in NSCLC: Current Therapeutic Applications and Progresses.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 24;24(7):6121. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076121. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unlocking Precision Medicine: Liquid Biopsy Advancements in Renal Cancer Detection and Monitoring.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 30;25(7):3867. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073867. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612677 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum Insights: Leveraging the Power of miRNA Profiling as an Early Diagnostic Tool for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Oct 10;15(20):4910. doi: 10.3390/cancers15204910. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37894277 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization Global Cancer Observatory-GLOBOCAN 2020. [(accessed on 16 April 2022)]. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

