Exploiting the Dixon Method for a Robust Breast and Fibro-Glandular Tissue Segmentation in Breast MRI
- PMID: 35885594
- PMCID: PMC9324146
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12071690
Exploiting the Dixon Method for a Robust Breast and Fibro-Glandular Tissue Segmentation in Breast MRI
Abstract
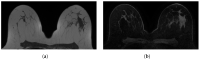
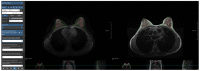
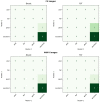
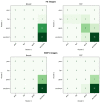
Automatic breast and fibro-glandular tissue (FGT) segmentation in breast MRI allows for the efficient and accurate calculation of breast density. The U-Net architecture, either 2D or 3D, has already been shown to be effective at addressing the segmentation problem in breast MRI. However, the lack of publicly available datasets for this task has forced several authors to rely on internal datasets composed of either acquisitions without fat suppression (WOFS) or with fat suppression (FS), limiting the generalization of the approach. To solve this problem, we propose a data-centric approach, efficiently using the data available. By collecting a dataset of T1-weighted breast MRI acquisitions acquired with the use of the Dixon method, we train a network on both T1 WOFS and FS acquisitions while utilizing the same ground truth segmentation. Using the "plug-and-play" framework nnUNet, we achieve, on our internal test set, a Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) of 0.96 and 0.91 for WOFS breast and FGT segmentation and 0.95 and 0.86 for FS breast and FGT segmentation, respectively. On an external, publicly available dataset, a panel of breast radiologists rated the quality of our automatic segmentation with an average of 3.73 on a four-point scale, with an average percentage agreement of 67.5%.
Keywords: MRI; breast; data-centric AI; deep learning; segmentation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Bakker M.F., de Lange S.V., Pijnappel R.M., Mann R.M., Peeters P.H.M., Monninkhof E.M., Emaus M.J., Loo C.E., Bisschops R.H.C., Lobbes M.B.I., et al. Supplemental MRI Screening for Women with Extremely Dense Breast Tissue. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019;381:2091–2102. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1903986. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mann R.M., Athanasiou A., Baltzer P.A.T., Camps-Herrero J., Clauser P., Fallenberg E.M., Forrai G., Fuchsjäger M.H., Helbich T.H., Killburn-Toppin F., et al. Breast cancer screening in women with extremely dense breasts recommendations of the European Society of Breast Imaging (EUSOBI) Eur. Radiol. 2022;32:4036–4045. doi: 10.1007/s00330-022-08617-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- American College of Radiology . ACR BI-RADS Atlas: Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System. 5th ed. American College of Radiology; Reston, VA, USA: 2013.
-
- Redondo A., Comas M., Macià F., Ferrer F., Murta-Nascimento C., Maristany M.T., Molins E., Sala M., Castells X. Inter- and intraradiologist variability in the BI-RADS assessment and breast density categories for screening mammograms. Br. J. Radiol. 2012;85:1465–1470. doi: 10.1259/bjr/21256379. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

