Anterior Ocular Biometrics as Measured by Ultrasound Biomicroscopy
- PMID: 35885715
- PMCID: PMC9318338
- DOI: 10.3390/healthcare10071188
Anterior Ocular Biometrics as Measured by Ultrasound Biomicroscopy
Abstract
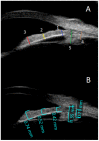
Background: High frequency ultrasonography (ultrasound biomicroscopy; UBM) is an ophthalmic diagnostic tool that can be used to measure the depth of the anterior segment (ASD), the anterior chamber angle (ACA), as well as thicknesses of the iris and the ciliary body (CB).
Methods: The anterior segment dimensions and thicknesses were measured by Sonomed 35-MHz.
Results: Measurements for 95 eyes from 52 adults were analyzed. The mean and median ASD and ACA were 2.91, 2.92 ± 0.41 mm and 34.1, 34.3 ± 12.1 degrees, respectively. The angle superiorly was wider than inferiorly (p = 0.04). At the root of the iris, the mid of the iris, and the juxtapupillary edge of the iris, the iris thicknesses (median, mean) were 0.40, 0.41 ± 0.1, 0.50, 0.51 ± 0.1, and 0.70, 0.71 ± 0.1 mm, respectively. The thicknesses of CB and CB together with the ciliary processes (median, mean), were 0.70, 0.71 ± 0.15 mm and 1.36, 1.41 ± 0.15 mm, respectively. The upper quadrant of both the iris and the CB was significantly thicker than the lower quadrant (p = 0.04).
Conclusions: Our biometric measurements for the anterior segment can be used as normative data for anterior segment depth and angle and iris and ciliary body thickness in normal eyes.
Keywords: anterior segment; ciliary body; iris; ultrasound biomicroscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest in this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ultrasound Biomicroscopy Measurements of the Normal Thickness for the Ciliary Body and the Iris in a Middle East Population.Clin Ophthalmol. 2022 Jan 10;16:101-109. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S297977. eCollection 2022. Clin Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35046635 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound biomicroscopic configurations of the anterior ocular segment in a population-based study the Kumejima Study.Ophthalmology. 2010 Sep;117(9):1720-8, 1728.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2010.01.045. Epub 2010 May 20. Ophthalmology. 2010. PMID: 20493530
-
Anterior Segment Morphology in Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma using Ultrasound Biomicroscopy.J Curr Glaucoma Pract. 2017 Sep-Dec;11(3):86-91. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10028-1230. Epub 2017 Oct 27. J Curr Glaucoma Pract. 2017. PMID: 29151682 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound biomicroscopy of the anterior segment.J Am Optom Assoc. 1996 Aug;67(8):469-79. J Am Optom Assoc. 1996. PMID: 8888877 Review.
-
An in-depth review on utilizing ultrasound biomicroscopy for assessing the iridocorneal angle and ciliary body in canines.Front Vet Sci. 2025 Feb 26;12:1501405. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2025.1501405. eCollection 2025. Front Vet Sci. 2025. PMID: 40078210 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Case report: Ultrasound biomicroscopy as a guide for the selection of injection sites for dexamethasone intravitreal implant (Ozurdex) for peripheral granulomatous ocular toxocariasis in children.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 May 16;10:1176585. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1176585. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37261126 Free PMC article.
-
Secondary Glaucoma Following Corneal Transplantation: A Comprehensive Review of Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Approaches.Cureus. 2024 Sep 21;16(9):e69882. doi: 10.7759/cureus.69882. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39439658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative analysis of iridocorneal angle in cats and dogs using ultrasound biomicroscopy: implications for glaucoma prevalence.BMC Vet Res. 2025 Mar 19;21(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s12917-025-04648-5. BMC Vet Res. 2025. PMID: 40102853 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound Biomicroscopy as a Novel, Potential Modality to Evaluate Anterior Segment Ophthalmic Structures during Spaceflight: An Analysis of Current Technology.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Mar 18;14(6):639. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14060639. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38535059 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

