A Formative Study of the Implementation of Whole Genome Sequencing in Northern Ireland
- PMID: 35885887
- PMCID: PMC9316942
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13071104
A Formative Study of the Implementation of Whole Genome Sequencing in Northern Ireland
Abstract
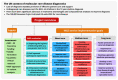
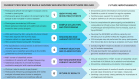
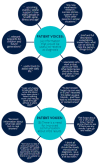
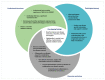
Background: The UK 100,000 Genomes Project was a transformational research project which facilitated whole genome sequencing (WGS) diagnostics for rare diseases. We evaluated experiences of introducing WGS in Northern Ireland, providing recommendations for future projects. Methods: This formative evaluation included (1) an appraisal of the logistics of implementing and delivering WGS, (2) a survey of participant self-reported views and experiences, (3) semi-structured interviews with healthcare staff as key informants who were involved in the delivery of WGS and (4) a workshop discussion about interprofessional collaboration with respect to molecular diagnostics. Results: We engaged with >400 participants, with detailed reflections obtained from 74 participants including patients, caregivers, key National Health Service (NHS) informants, and researchers (patient survey n = 42; semi-structured interviews n = 19; attendees of the discussion workshop n = 13). Overarching themes included the need to improve rare disease awareness, education, and support services, as well as interprofessional collaboration being central to an effective, mainstreamed molecular diagnostic service. Conclusions: Recommendations for streamlining precision medicine for patients with rare diseases include administrative improvements (e.g., streamlining of the consent process), educational improvements (e.g., rare disease training provided from undergraduate to postgraduate education alongside genomics training for non-genetic specialists) and analytical improvements (e.g., multidisciplinary collaboration and improved computational infrastructure).
Keywords: collaboration; genomics; multiomics; public health; rare disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Improvements needed to support people living and working with a rare disease in Northern Ireland: current rare disease support perceived as inadequate.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2020 Nov 9;15(1):315. doi: 10.1186/s13023-020-01559-6. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2020. PMID: 33168042 Free PMC article.
-
Variation Exists in Service Delivery: Similarities and Differences in the Provision of a Whole Genome Sequencing Service for Paediatric Rare Disease Patients in the National Health Service in England.Public Health Genomics. 2025;28(1):1-18. doi: 10.1159/000542027. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Public Health Genomics. 2025. PMID: 39522508
-
Identifying barriers and opportunities to facilitate the uptake of whole genome sequencing in paediatric haematology and oncology practice.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Nov 6;24(1):1273. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-06219-y. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 39506754 Free PMC article.
-
Operational models and criteria for incorporating microbial whole genome sequencing in hospital microbiology - A systematic literature review.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019 Sep;25(9):1086-1095. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2019.04.019. Epub 2019 Apr 27. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019. PMID: 31039443
-
Whole genome sequencing in oncology: using scenario drafting to explore future developments.BMC Cancer. 2021 May 1;21(1):488. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08214-8. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33933021 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Stakeholder Perceptions of Complementary and Integrative Medicines from People Living with Rare Diseases in Northern Ireland: A Mixed Methods Study.Complement Med Res. 2024;31(2):107-115. doi: 10.1159/000535480. Epub 2023 Dec 5. Complement Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38052188 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of genomic medicine to mainstream patient care within the UK National Health Service.Ulster Med J. 2024 Nov;93(3):111-118. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Ulster Med J. 2024. PMID: 39606143 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Worldometer. [(accessed on 20 April 2022)]. Available online: https://www.worldometers.info/
-
- Orphanet Nomenclature. [(accessed on 14 May 2022)]. Available online: http://www.orphadata.org/cgi-bin/ORPHAnomenclature.html.
-
- Blöß S., Klemann C., Rother A.-K., Mehmecke S., Schumacher U., Mücke U., Mücke M., Stieber C., Klawonn F., Kortum X., et al. Diagnostic needs for rare diseases and shared prediagnostic phenomena: Results of a German-wide expert Delphi survey. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0172532. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0172532. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

