MicroRNA Processing Pathway-Based Polygenic Score for Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma in the Volga-Ural Region Populations of Eurasian Continent
- PMID: 35886064
- PMCID: PMC9324265
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13071281
MicroRNA Processing Pathway-Based Polygenic Score for Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma in the Volga-Ural Region Populations of Eurasian Continent
Abstract
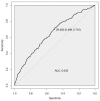
The polygenic scores (PGSs) are developed to help clinicians in distinguishing individuals at high risk of developing disease outcomes from the general population. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) is a complex disorder that involves numerous biological pathways, one of the most important of which is responsible for the microRNA biogenesis machinery. Here, we defined the biological-pathway-specific PGS in a case-control study of ccRCC in the Volga-Ural region of the Eurasia continent. We evaluated 28 DNA SNP variants, located in microRNA biogenesis genes, in 464 individuals with clinically diagnosed ccRCC and 1042 individuals without the disease. Individual genetic risks were defined using the SNP-variant effects derived from the ccRCC association analysis. The final weighted and unweighted PGS models were based on 21 SNPs, and 7 SNPs were excluded due to high LD. In our dataset, microRNA-machinery-weighted PGS revealed 1.69-fold higher odds (95% CI [1.51-1.91]) for ccRCC risk in individuals with ccRCC compared with controls with a p-value of 2.0 × 10-16. The microRNA biogenesis pathway weighted PGS predicted the risk of ccRCC with an area under the curve (AUC) = 0.642 (95%nCI [0.61-0.67]). Our findings indicate that DNA variants of microRNA machinery genes modulate the risk of ccRCC in Volga-Ural populations. Moreover, larger powerful genome-wide association studies are needed to reveal a wider range of genetic variants affecting microRNA processing. Biological-pathway-based PGSs will advance the development of innovative screening systems for future stratified medicine approaches in ccRCC.
Keywords: genetic risk score; renal cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA Expression Signatures in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: High-Throughput Searching for Key miRNA Markers in Patients from the Volga-Ural Region of Eurasian Continent.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 7;24(8):6909. doi: 10.3390/ijms24086909. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108073 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Polygenic Risk Score for Prediction of Childhood Onset and Severity of Asthma.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 26;26(1):103. doi: 10.3390/ijms26010103. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39795959 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-30a-5pme: a novel diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for clear cell renal cell carcinoma in tissue and urine samples.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Jun 1;39(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01600-3. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32487203 Free PMC article.
-
The biological roles and clinical implications of microRNAs in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Jun;233(6):4458-4465. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26347. Epub 2017 Dec 26. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29215721 Review.
-
Does chromophobe renal cell carcinoma have better survival than clear cell renal cell carcinoma? A clinical-based cohort study and meta-analysis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2016 Feb;48(2):191-9. doi: 10.1007/s11255-015-1161-3. Epub 2015 Nov 20. Int Urol Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26589610 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA Expression Signatures in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: High-Throughput Searching for Key miRNA Markers in Patients from the Volga-Ural Region of Eurasian Continent.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 7;24(8):6909. doi: 10.3390/ijms24086909. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108073 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ferlay J., Ervik M., Lam F., Colombet M., Mery L., Piñeros M., Znaor A., Soerjomataram I., Bray F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: 2020. [(accessed on 22 March 2022)]. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials