The Role of RNA Modification in HIV-1 Infection
- PMID: 35886919
- PMCID: PMC9317671
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23147571
The Role of RNA Modification in HIV-1 Infection
Abstract
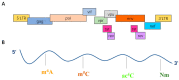
RNA plays an important role in biology, and more than 170 RNA modifications have been identified so far. Post-transcriptional modification of RNA in cells plays a crucial role in the regulation of its stability, transport, processing, and gene expression. So far, the research on RNA modification and the exact role of its enzymes is becoming more and more comprehensive. Human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) is an RNA virus and the causative agent of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), which is one of the most devastating viral pandemics in history. More and more studies have shown that HIV has RNA modifications and regulation of its gene expression during infection and replication. This review focuses on several RNA modifications and their regulatory roles as well as the roles that different RNA modifications play during HIV-1 infection, in order to find new approaches for the development of anti-HIV-1 therapeutics.
Keywords: HIV-1 infection; RNA methylation modification; RNA modification; RNA virus; post-transcriptional modification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The regulation of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 gene expression.Eur J Biochem. 1996 Sep 15;240(3):491-507. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.0491h.x. Eur J Biochem. 1996. PMID: 8856047 Review.
-
The Relevance of Post-Transcriptional Mechanisms in HIV Latency Reversal.Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(28):4103-4111. doi: 10.2174/1381612823666170803102355. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 28782474 Review.
-
Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by regulated expression of a polymeric Tat activation response RNA decoy as a strategy for gene therapy in AIDS.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):8000-4. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.8000. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993. PMID: 8367455 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of expression of human immunodeficiency virus.New Biol. 1990 Jan;2(1):20-31. New Biol. 1990. PMID: 2078551 Review.
-
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 2-mediated inhibition of HIV type 1: a new approach to gene therapy of HIV-infection.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Apr 30;93(9):4486-91. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.9.4486. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996. PMID: 8633095 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Epitranscriptomics on Antiviral Innate Immunity.Viruses. 2022 Jul 28;14(8):1666. doi: 10.3390/v14081666. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36016289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An HIV-1 Reference Epitranscriptome.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 21:2025.01.30.635805. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.30.635805. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39975020 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Characterizing transcripts of HIV-1 different substrains using direct RNA sequencing.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 17;10(20):e39474. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39474. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39512311 Free PMC article.
-
Detection, molecular function and mechanisms of m5C in cancer.Clin Transl Med. 2025 Mar;15(3):e70239. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.70239. Clin Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40008496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N4-acetylcytidine coordinates with NP1 and CPSF5 to facilitate alternative RNA processing during the replication of minute virus of canines.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Mar 20;53(6):gkaf229. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf229. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40167508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rehman M.U., Hong K.J., Tayara H., Chong K.T. m6A-NeuralTool: Convolution Neural Tool for RNA N6-Methyladenosine Site Identification in Different Species. IEEE Access. 2021;9:17779–17786. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3054361. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

