Effect of Pre-Induced Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Coated Cellulose/Collagen Nanofibrous Nerve Conduit on Regeneration of Transected Facial Nerve
- PMID: 35886987
- PMCID: PMC9318960
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23147638
Effect of Pre-Induced Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Coated Cellulose/Collagen Nanofibrous Nerve Conduit on Regeneration of Transected Facial Nerve
Abstract
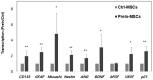
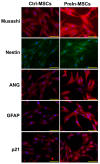
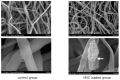
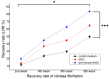
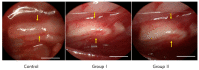
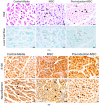
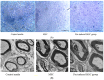
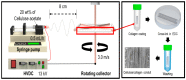
(1) Objective: In order to evaluate the effect of a pre-induced mesenchymal stem cell (MSC)-coated cellulose/collagen nanofibrous nerve conduit on facial nerve regeneration in a rat model both in vitro and in vivo. (2) Methods: After fabrication of the cellulose/collagen nanofibrous conduit, its lumen was coated with either MSCs or pre-induced MSCs. The nerve conduit was then applied to the defective main trunk of the facial nerve. Rats were randomly divided into three treatment groups (n = 10 in each): cellulose/collagen nanofiber (control group), cellulose/collagen nanofiber/MSCs (group I), and cellulose/collagen nanofiber/pre-induced MSCs (group II). (3) Results Fibrillation of the vibrissae of each group was observed, and action potential threshold was compared 8 weeks post-surgery. Histopathological changes were also observed. Groups I and II showed better recovery of vibrissa fibrillation than the control group. (4) Conclusions: Group II, treated with the pre-induced MSC-coated cellulose/collagen nanofibrous nerve conduit, showed the highest degree of recovery based on functional and histological evaluations.
Keywords: cellulose; collagen; nanofibrous nerve conduit; nerve regeneration; pre-induced mesenchymal stem cell.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Condition Medium Loaded on PCL Nanofibrous Scaffold Promoted Nerve Regeneration After Sciatic Nerve Transection in Male Rats.Neurotox Res. 2021 Oct;39(5):1470-1486. doi: 10.1007/s12640-021-00391-5. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Neurotox Res. 2021. PMID: 34309780
-
Bacterial cellulose tubes as a nerve conduit for repairing complete facial nerve transection in a rat model.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 Jan;277(1):277-283. doi: 10.1007/s00405-019-05637-9. Epub 2019 Oct 8. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020. PMID: 31595316
-
Bioabsorbable nerve conduits three-dimensionally coated with human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neural stem/progenitor cells promote peripheral nerve regeneration in rats.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 18;11(1):4204. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83385-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33602991 Free PMC article.
-
Nerve Regeneration Through Differentiation of Endometrial-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells into Nerve-Like Cells Using Polyacrylonitrile/Chitosan Conduit and Berberine in a Rat Sciatic Nerve Injury Model.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Feb;62(2):1493-1510. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04344-9. Epub 2024 Jul 13. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 38997619
-
Chitosan-film associated with mesenchymal stem cells enhanced regeneration of peripheral nerves: A rat sciatic nerve model.J Chem Neuroanat. 2018 Mar;88:46-54. doi: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2017.10.003. Epub 2017 Oct 26. J Chem Neuroanat. 2018. PMID: 29107096
Cited by
-
Advances in Regenerative Dentistry Approaches: An Update.Int Dent J. 2024 Feb;74(1):25-34. doi: 10.1016/j.identj.2023.07.008. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Int Dent J. 2024. PMID: 37541918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Synergistic Effect of Polydeoxyribonucleotides with Low-Level Lasers on the Regeneration of Crush-Injured Facial Nerves.J Clin Med. 2025 Mar 1;14(5):1678. doi: 10.3390/jcm14051678. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40095740 Free PMC article.
-
Porous Organic Materials in Tissue Engineering: Recent Advances and Applications for Severed Facial Nerve Injury Repair.Molecules. 2024 Jan 23;29(3):566. doi: 10.3390/molecules29030566. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38338311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress on composite nerve guidance conduits with immune-regulatory functions.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 10;16:1622508. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1622508. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40557153 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Metformin on the Functional and Electrophysiological Recovery of Crush Injury-Induced Facial Nerve Paralysis in Diabetic Rats.J Pers Med. 2023 Aug 27;13(9):1317. doi: 10.3390/jpm13091317. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37763084 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Farzamfar S., Naseri-Nosar M., Vaez A., Esmaeilpour F., Ehterami A., Sahrapeyma H., Samadian H., Hamidieh A.-A., Ghorbani S., Goodarzi A. Neural tissue regeneration by a gabapentin-loaded cellulose acetate/gelatin wet-electrospun scaffold. Cellulose. 2018;25:1229–1238. doi: 10.1007/s10570-017-1632-z. - DOI
-
- Urrutia D.N., Caviedes P., Mardones R., Minguell J.J., Vega-Letter A.M., Jofre C.M. Comparative study of the neural differentiation capacity of mesenchymal stromal cells from different tissue sources: An approach for their use in neural regeneration therapies. PLoS ONE. 2019;14:e0213032. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213032. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

