Phagocytosis of Erythrocytes from Gaucher Patients Induces Phenotypic Modifications in Macrophages, Driving Them toward Gaucher Cells
- PMID: 35886988
- PMCID: PMC9319206
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23147640
Phagocytosis of Erythrocytes from Gaucher Patients Induces Phenotypic Modifications in Macrophages, Driving Them toward Gaucher Cells
Abstract
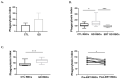
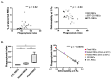
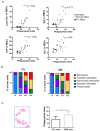
Gaucher disease (GD) is caused by glucocerebrosidase deficiency leading to the accumulation of sphingolipids in macrophages named "Gaucher's Cells". These cells are characterized by deregulated expression of cell surface markers, abnormal secretion of inflammatory cytokines, and iron sequestration. These cells are known to infiltrate tissues resulting in hematological manifestations, splenomegaly, and bone diseases. We have already demonstrated that Gaucher red blood cells exhibit altered properties suggesting their key role in GD clinical manifestations. We hypothesized that Gaucher's erythrocytes could be prone to premature destruction by macrophages contributing to the formation of altered macrophages and Gaucher-like cells. We conducted in vitro experiments of erythrophagocytosis using erythrocytes from Gaucher's patients or healthy donors. Our results showed an enhanced erythrophagocytosis of Gaucher red blood cells compared to healthy red blood cells, which is related to erythrocyte sphingolipids overload and reduced deformability. Importantly, we showed elevated expression of the antigen-presenting molecules CD1d and MHC-II and of the iron-regulator hepcidin in macrophages, as well as enhanced secretion of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1β after phagocytosis of GD erythrocytes. These results strongly suggested that erythrophagocytosis in GD contribute to phenotypic modifications in macrophages. This present study shows that erythrocytes-macrophages interactions may be crucial in GD pathophysiology and pathogenesis.
Keywords: Gaucher disease; erythrophagocytosis; macrophages; red blood cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Abnormal properties of red blood cells suggest a role in the pathophysiology of Gaucher disease.Blood. 2013 Jan 17;121(3):546-55. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-07-442467. Epub 2012 Dec 3. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23212518
-
Effects of sphingolipids overload on red blood cell properties in Gaucher disease.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Sep;24(17):9726-9736. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15534. Epub 2020 Aug 7. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32767726 Free PMC article.
-
Gaucher iPSC-derived macrophages produce elevated levels of inflammatory mediators and serve as a new platform for therapeutic development.Stem Cells. 2014 Sep;32(9):2338-49. doi: 10.1002/stem.1732. Stem Cells. 2014. PMID: 24801745 Free PMC article.
-
Defective Sphingolipids Metabolism and Tumor Associated Macrophages as the Possible Links Between Gaucher Disease and Blood Cancer Development.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 15;20(4):843. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040843. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30781349 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gaucher's disease and cancer: a sphingolipid perspective.Crit Rev Oncog. 2013;18(3):221-34. doi: 10.1615/critrevoncog.2013005814. Crit Rev Oncog. 2013. PMID: 23510065 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GBA1 Gene Mutations in α-Synucleinopathies-Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Pathology and Their Clinical Significance.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 20;24(3):2044. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032044. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review on Gaucher disease: therapeutic potential of β-glucocerebrosidase-targeted mRNA/saRNA approach.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Mar 17;20(6):2111-2129. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.87741. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38617529 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hereditary Hyperferritinemia.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 29;24(3):2560. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032560. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768886 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eryptosis in Liver Diseases: Contribution to Anemia and Hypercoagulation.Med Sci (Basel). 2025 Aug 12;13(3):125. doi: 10.3390/medsci13030125. Med Sci (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40843747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physiology of Red Cell Lineage: From Erythroblast Progenitors to Mature Red Blood Cell.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 3;24(11):9715. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119715. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barton N.W., Brady R.O., Dambrosia J.M., Di Bisceglie A.M., Doppelt S.H., Hill S.C., Mankin H.J., Murray G.J., Parker R.I., Argoff C.E., et al. Replacement therapy for inherited enzyme deficiency-macrophage-targeted glucocerebrosidase for Gaucher’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991;324:1464–1470. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199105233242104. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

