Experience with Photodynamic Therapy Using Indocyanine Green Liposomes for Refractory Cancer
- PMID: 35887536
- PMCID: PMC9318386
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm12071039
Experience with Photodynamic Therapy Using Indocyanine Green Liposomes for Refractory Cancer
Abstract
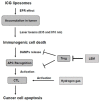
We reported the development of an effective cancer treatment using a multidisciplinary treatment, including photodynamic therapy (PDT) with indocyanine green (ICG) liposomes and a combination of Lentinula edodes mycelia (LEM) and hydrogen gas inhalation therapy. ICG liposomes were prepared by adding 5 mg of ICG to 50 mL liposomes. Later, 25 mL of ICG liposomes were diluted with 250 mL of 5% glucose solution and administered intravenously to the patient. We selected the multi-laser delivery system (MLDS), a laser irradiator for performing PDT. Further, the patients received a combination of LEM and hydrogen gas inhalation therapy throughout the treatment. We reported two cases of PDT therapy, one with middle intrathoracic esophagus carcinoma and the other with hypopharyngeal cancer. In the first case, the MLDS laser was directly attached to the endoscope and directed to the cancer area with wavelengths of 810 nm. After the treatment, a biopsy demonstrated no tumor recurrence. In the second case, the patient was treated with endovascular PDT using ICG liposomes and MLDS fiber optics. Later, tumor shrinkage was demonstrated after the first round and disappeared after six months. In conclusion, the present findings suggest that the effect of PDT using ICG liposomes with LEM and hydrogen gas may eradicate cancer without burdening patients by enhancing tumor immunity.
Keywords: Lentinula edodes mycelia; esophagus carcinoma; hydrogen gas; hypopharyngeal cancer; indocyanine green liposomes; multi-laser delivery system; photodynamic therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Indocyanine green loaded liposome nanocarriers for photodynamic therapy using human triple negative breast cancer cells.Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2014 Jun;11(2):193-203. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2014.02.001. Epub 2014 Mar 19. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2014. PMID: 24657627
-
Photodynamic therapy with paclitaxel-encapsulated indocyanine green-modified liposomes for breast cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 Mar 7;14:1365305. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1365305. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38515576 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan-coated liposomes to stabilize and enhance transdermal delivery of indocyanine green for photodynamic therapy of melanoma.Carbohydr Polym. 2019 Nov 15;224:115143. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115143. Epub 2019 Aug 2. Carbohydr Polym. 2019. PMID: 31472877
-
Treatment of near-infrared photodynamic therapy using a liposomally formulated indocyanine green derivative for squamous cell carcinoma.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 7;10(4):e0122849. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122849. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25850029 Free PMC article.
-
ROS-responsive liposomes with NIR light-triggered doxorubicin release for combinatorial therapy of breast cancer.J Nanobiotechnology. 2021 May 11;19(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s12951-021-00877-6. J Nanobiotechnology. 2021. PMID: 33975609 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Optimizing Photosensitizer Delivery for Effective Photodynamic Inactivation of Klebsiella pneumoniae Under Lung Surfactant Conditions.Pathogens. 2025 Jun 21;14(7):618. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14070618. Pathogens. 2025. PMID: 40732666 Free PMC article.
-
Photodynamic Therapy Using IR-783 Liposomes for Advanced Tongue and Breast Cancers in Humans.J Funct Biomater. 2024 Dec 2;15(12):363. doi: 10.3390/jfb15120363. J Funct Biomater. 2024. PMID: 39728163 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of photodynamic therapy on immune system in cancer - an update.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 28;15:1335920. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1335920. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38481994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined Ferritin Nanocarriers with ICG for Effective Phototherapy Against Breast Cancer.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 May 14;19:4263-4278. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S445334. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38766663 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Use of Cisplatin Liposomes for Patients With Refractory Advanced Cancer.Cureus. 2024 Nov 6;16(11):e73181. doi: 10.7759/cureus.73181. eCollection 2024 Nov. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39650995 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Assis L., Moretti A.I., Abrahão T.B., Cury V., Souza H.P., Hamblin M.R., Parizotto N.A. Low-level laser therapy (808 nm) reduces inflammatory response and oxidative stress in rat tibialis anterior muscle after cryolesion. Lasers Surg. Med. 2012;44:726–735. doi: 10.1002/lsm.22077. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

