Predicting Loss of Efficacy after Non-Medical Switching: Correlation between Circulating TNF-α Levels and SB4 in Etanercept to SB4 Switchers and Naïve Patients with Rheumatic Disease
- PMID: 35887671
- PMCID: PMC9316161
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm12071174
Predicting Loss of Efficacy after Non-Medical Switching: Correlation between Circulating TNF-α Levels and SB4 in Etanercept to SB4 Switchers and Naïve Patients with Rheumatic Disease
Erratum in
-
Correction: Benucci et al. Predicting Loss of Efficacy after Non-Medical Switching: Correlation between Circulating TNF-α Levels and SB4 in Etanercept to SB4 Switchers and Naïve Patients with Rheumatic Disease. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1174.J Pers Med. 2023 Jan 18;13(2):168. doi: 10.3390/jpm13020168. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 36836609 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: We investigated how the non-medical switching (NMS) between Etanercept (ETN)/originator and SB4/biosimilar affects treatment efficacy in a rheumatic disease (RD) cohort, evaluating some laboratory parameters as loss of efficacy predictors after NMS.
Methods: We enrolled 124 patients with RD (rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, psoriatic arthritis): 79 switchers from ETN/originator to SB4 and 45 naïve patients receiving SB4 (first biological treatment). At baseline, 6 (T1), and 12 months (T2), clinical and laboratory parameters were evaluated.
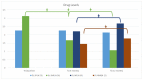
Results: In naïve patients, TNF-α significantly increased at T1 in responders (NR) and non-responders (NNR). TNF-α was lower in NNR than in NR at T1 and T2. In NR and NNR, drug levels (DL) increased between T1 and T2. However, DLs were lower in NNR than in NR at T1 and T2. TNF-α was higher in switcher responders (SR) than in non-responders (SNR) at T1 and T2. In SNR, DLs were higher at baseline than in SR, but they decreased significantly at T1 and T2.
Conclusions: We observed a decrease in DL and TNF-α levels after NMS in SNR. Moreover, in naïve patients, DL and TNF-α levels were higher in NR than in NNR. Monitoring DL and TNF-α levels may represent a future precision medicine approach to predict loss of efficacy after NMS.
Keywords: Etanercept/SB4; biosimilars; disease activity; loss of efficacy; non-medical switching; precision medicine; rheumatic disease.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- European Medicines Agency (EMA) Biosimilars in EU. Information Guide for Healthcare Professionals. [(accessed on 1 January 2022)]. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/new-guide-biosimilar-medicines-healthc....
-
- US Food and Drug Administration Biosimilars. [(accessed on 1 January 2022)]; Available online: https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/DevelopmentApprovalProcess/HowDrugsareDevelope...
-
- Ruff L., Rezk M.F., Uhlig T., Gommers J.W. Budget impact analysis of an etanercept biosimilar for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in Europe. Value Health. 2015;18:A639. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2015.09.2276. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous