Proximal Median Nerve Compression in the Differential Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- PMID: 35887752
- PMCID: PMC9317082
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11143988
Proximal Median Nerve Compression in the Differential Diagnosis of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Abstract
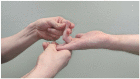
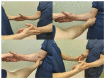
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the most common median nerve compression neuropathy. Its symptoms and clinical presentation are well known. However, symptoms at median nerve distribution can also be caused by a proximal problem. Pronator syndrome (PS) and anterior interosseous nerve syndrome (AINS) with their typical characteristics have been thought to explain proximal median nerve problems. Still, the literature on proximal median nerve compressions (PMNCs) is conflicting, making this classic split too simple. This review clarifies that PMNCs should be understood as a spectrum of mild to severe nerve lesions along a branching median nerve, thus causing variable symptoms. Clear objective findings are not always present, and therefore, diagnosis should be based on a more thorough understanding of anatomy and clinical testing. Treatment should be planned according to each patient's individual situation. To emphasize the complexity of causes and symptoms, PMNC should be named proximal median nerve syndrome.
Keywords: carpal tunnel syndrome; median nerve entrapment; median neuropathy; neuralgic amyotrophy; pronator syndrome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

