Assessment of Satisfaction, Compliance and Side Effects among Long-Term Orthokeratology Wearers
- PMID: 35887890
- PMCID: PMC9321806
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11144126
Assessment of Satisfaction, Compliance and Side Effects among Long-Term Orthokeratology Wearers
Abstract
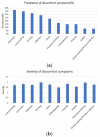
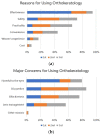
Purpose: This study aims to assess the satisfaction, compliance, and side effects among the long-term orthokeratology (Ortho-K) users in a tertiary hospital in Taiwan and analyze the side effects and related risk factors. Methods: Children and their guardians were assessed using a structured and validated questionnaire inquiring about background information, wear and care behaviors, daily activities, satisfaction, and related concerns. Clinical information, including refractive data and side effects, was obtained through patient medical files. Results: Three hundred and five school-aged patients were enrolled, and the average age was 13.13 ± 3.39 years, with an average wearing period of 17.1 ± 8.1 months. Over 83% of the subjects had clear daytime vision all day, around 88% felt satisfied or very satisfied with the results, and 98% exhibited a willingness to continue wearing the Ortho-K lenses. Most guardians (83%) were pleased with the controlling effect of myopic progression. Initial spherical equivalent and regular cleaning of the lens protein significantly correlated with clear day vision. Wearing >6 days/week correlated with less risk of lens binding. Based on the questionnaire, the main reasons for using Ortho-K were effectiveness, safety, and practicality, while the major concerns were discomfort, harmful to the eyes, and no effect. Conclusion: With a comprehensive care program from practitioners and good compliance of users, Ortho-K could be the most effective and satisfactory option for myopic children in Taiwan.
Keywords: compliance; myopia; orthokeratology (Ortho-k); satisfaction; survey.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An assessment of consecutively presenting orthokeratology patients in a Hong Kong based private practice.Clin Exp Optom. 2003 Sep;86(5):331-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1444-0938.2003.tb03129.x. Clin Exp Optom. 2003. PMID: 14558855
-
Analysis of parental decisions to use orthokeratology for myopia control in successful wearers.Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2021 Jan;41(1):3-12. doi: 10.1111/opo.12744. Epub 2020 Oct 16. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt. 2021. PMID: 33063901 Review.
-
Vision-related quality of life of Chinese children undergoing orthokeratology treatment compared to single vision spectacles.Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2021 Aug;44(4):101350. doi: 10.1016/j.clae.2020.07.001. Epub 2020 Jul 13. Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2021. PMID: 32674999
-
Trajectories of myopia control and orthokeratology compliance among parents with myopic children.Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2021 Aug;44(4):101360. doi: 10.1016/j.clae.2020.08.004. Epub 2020 Oct 3. Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2021. PMID: 33023822
-
Interventions to slow progression of myopia in children.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 13;1(1):CD004916. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004916.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 31930781 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of repeated low-level red light in myopia prevention and myopia control.Br J Ophthalmol. 2024 Aug 22;108(9):1299-1305. doi: 10.1136/bjo-2023-324260. Br J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38631861 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Research Hotspots of Acupuncture Treatment for Myopia Over the Past Decade: A Bibliometric Analysis (2014-2023).Clin Ophthalmol. 2024 Oct 22;18:2985-2997. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S483740. eCollection 2024. Clin Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39463850 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chinese parents' knowledge, attitude, and practice of myopia control: 2023 update.BMC Public Health. 2025 Feb 25;25(1):779. doi: 10.1186/s12889-025-22003-z. BMC Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40001101 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources