Thrombelastography Compared with Multiple Impedance Aggregometry to Assess High On-Clopidogrel Reactivity in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
- PMID: 35888001
- PMCID: PMC9320091
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11144237
Thrombelastography Compared with Multiple Impedance Aggregometry to Assess High On-Clopidogrel Reactivity in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Abstract
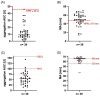
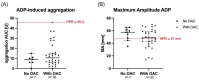
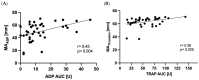
Background: High on-clopidogrel platelet reactivity (HPR) following percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is associated with increased ischemic risk. It is unclear whether conventional definitions of HPR apply to patients with concomitant oral anticoagulation (OAC). This study aimed to compare the performance of multiple platelet aggregometry (MEA) and thrombelastography (TEG) to detect HPR in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) and indication for an OAC. Methods: In this observational single-center cohort study, MEA and TEG were performed in patients with AF with an indication for OAC on day 1 to 3 after PCI. The primary outcome was HPR as assessed by MEA (ADP area under the curve ≥ 46 units [U]) or TEG (MAADP ≥ 47 mm), respectively. The secondary exploratory outcomes were a composite of all-cause death, myocardial infarction (MI) or stroke and bleeding, as defined by the International Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis, at 6 months. Results: Platelet function of 39 patients was analyzed. The median age was 78 (interquartile range [IQR] was 72−82) years. 25 (64%) patients were male, and 19 (49%) presented with acute coronary syndrome. All patients received acetylsalicylic acid and clopidogrel prior to PCI. Median (IQR) ADP-induced aggregation, MAADP, TRAP-induced aggregation, and MAthrombin were 9 (6−15) U, 50 (43−60) mm, 54 (35−77) U and 65 (60−67) mm, respectively. The rate of HPR was significantly higher if assessed by TEG compared with MEA (25 [64%] vs. 1 [3%]; p < 0.001). Within 6 months, four (10%) deaths, one (3%) MI and nine (23%) bleeding events occurred. Conclusion: In patients with AF undergoing PCI, the rates of HPR detected by TEG were significantly higher compared with MEA. Conventional cut-off values for HPR as proposed by consensus documents may need to be re-evaluated for this population at high ischemic and bleeding risk. Further studies are needed to assess the association with outcomes.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; multiple electrode aggregometry; percutaneous coronary intervention; platelet reactivity; thrombelastography.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hindricks G., Potpara T., Dagres N., Arbelo E., Bax J.J., Blomström-Lundqvist C., Boriani G., Castella M., Dan G.A., Dilaveris P.E., et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) Eur. Heart J. 2021;42:373–498. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehaa612. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Vranckx P., Valgimigli M., Eckardt L., Tijssen J., Lewalter T., Gargiulo G., Batushkin V., Campo G., Lysak Z., Vakaliuk I., et al. Edoxaban-based versus vitamin K antagonist-based antithrombotic regimen after successful coronary stenting in patients with atrial fibrillation (ENTRUST-AF PCI): A randomised, open-label, phase 3b trial. Lancet. 2019;394:1335–1343. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31872-0. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

