Plasma-Saline Water Interaction: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 35888319
- PMCID: PMC9324451
- DOI: 10.3390/ma15144854
Plasma-Saline Water Interaction: A Systematic Review
Abstract
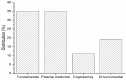
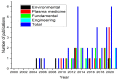
Plasma-liquid interaction research has developed substantially in recent years due, mostly, to the numerous applications of cold atmospheric plasma (CAP). Plasma-liquid interactions are influenced by the concentrations of the ionic species present in the liquid environment, and few studies have paid attention to saline water, which generally mediates the reactions in many plasma applications. Therefore, the present review aims to explore the main results and the influence of variables on the modification of properties of saline water by CAP sources following the guidelines of the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA). The searches were carried out in the Scopus, Science Direct, and Web of Science databases, resulting in the inclusion of 37 studies. The main effects of the interaction between CAP and saline water are (i) the production of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS); (ii) the increase in conductivity and decrease in pH, directly proportional to the increase in discharge voltage; (iii) and the effective area of interaction and the shortest distance between electrode and solution. Other effects are the localized evaporation and crystallization of salts, which make the interaction between plasma and saline water a promising field in the development of technologies for desalination and improvement of liquid properties.
Keywords: DBD; PRISMA; atmospheric plasma; corona discharge; saline water.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Yang Y., Cho Y.I., Fridman A. Plasma Discharge in Liquid. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2012.
-
- Mariotti D., Patel J., Švrček V., Maguire P. Plasma-liquid interactions at atmospheric pressure for nanomaterials synthesis and surface engineering. Plasma Process. Polym. 2012;9:1074–1085. doi: 10.1002/ppap.201200007. - DOI
-
- Surowsky B., Schlüter O., Knorr D. Interactions of Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma with Solid and Liquid Food Systems: A Review. Food Eng. Rev. 2015;7:82–108. doi: 10.1007/s12393-014-9088-5. - DOI
-
- Vandenabeele C.R., Lucas S. Technological challenges and progress in nanomaterials plasma surface modification—A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2020;139:100521. doi: 10.1016/j.mser.2019.100521. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

