Microwave-Assisted Solvent Bonding for Polymethyl Methacrylate Microfluidic Device
- PMID: 35888948
- PMCID: PMC9320591
- DOI: 10.3390/mi13071131
Microwave-Assisted Solvent Bonding for Polymethyl Methacrylate Microfluidic Device
Abstract
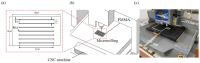
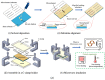
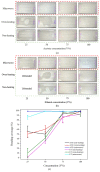
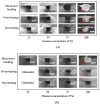
This paper demonstrated a microwave-assisted solvent bonding method that uses organic solvent to seal the thermoplastic substrates with microwave assistance. This direct bonding is a simple and straightforward process that starts with solvent application followed by microwave irradiation without the need for expensive facilities or complex procedures. The organic solvent applied at the bonding interface is used in dissolving and dielectric heating of the thermoplastic surfaces to seal the thermoplastic substrates under microwave assistance. We evaluated acetone and ethanol to seal the polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) microfluidic device. The bonding performance, such as bonding coverage, geometry stability, and bonding strength (tensile) were observed and compared with the oven-heating and non-heating control experiments under the same force applications. Results showed that the microwave-assisted solvent bonding method presents a high bonding yield (maximum > 99%) and bonding strength (maximum ~2.77 MPa) without microchannel distortion, which can be used for various microfluidic applications.
Keywords: microwave heating; polymer microfluidics; solvent bonding; thermoplastic bonding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Pressure-Free Assembling of Poly(methyl methacrylate) Microdevices via Microwave-Assisted Solvent Bonding and Its Biomedical Applications.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Dec 20;11(12):526. doi: 10.3390/bios11120526. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34940283 Free PMC article.
-
Solvent Bonding for Fabrication of PMMA and COP Microfluidic Devices.J Vis Exp. 2017 Jan 17;(119):55175. doi: 10.3791/55175. J Vis Exp. 2017. PMID: 28117831 Free PMC article.
-
PMMA Solution Assisted Room Temperature Bonding for PMMA⁻PC Hybrid Devices.Micromachines (Basel). 2017 Sep 20;8(9):284. doi: 10.3390/mi8090284. Micromachines (Basel). 2017. PMID: 30400474 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Thermoplastic Microfluidic Bonding.Micromachines (Basel). 2022 Mar 20;13(3):486. doi: 10.3390/mi13030486. Micromachines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35334777 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidic Modules Integrated with Microwave Components-Overview of Applications from the Perspective of Different Manufacturing Technologies.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Mar 2;21(5):1710. doi: 10.3390/s21051710. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33801309 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fabrication of a Three-Dimensional Microfluidic System from Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) Using an Intermiscibility Vacuum Bonding Technique.Micromachines (Basel). 2024 Mar 28;15(4):454. doi: 10.3390/mi15040454. Micromachines (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675265 Free PMC article.
-
Nonthermal Effect of Microwave Processing Enhances Interface Reactivity and Microchannel Integrity: Low-Temperature Rapid Bonding of PMMA Microfluidic Devices.ACS Omega. 2024 Dec 18;10(8):7662-7671. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c07013. eCollection 2025 Mar 4. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 40060821 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Materials Made by Combining Hydrogels (Cross-Linked Polyacrylamides) and Conducting Polymers (Polyanilines)-A Critical Review.Polymers (Basel). 2023 May 9;15(10):2240. doi: 10.3390/polym15102240. Polymers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37242814 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Convery N., Gadegaard N. 30 years of microfluidics. Micro Nano Eng. 2019;2:76–91. doi: 10.1016/j.mne.2019.01.003. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

