Microbial Inoculation Improves Growth, Nutritional and Physiological Aspects of Glycine max (L.) Merr
- PMID: 35889105
- PMCID: PMC9316164
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms10071386
Microbial Inoculation Improves Growth, Nutritional and Physiological Aspects of Glycine max (L.) Merr
Abstract
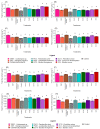
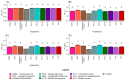
Considering a scenario where there is a low availability and increasing costs of fertilizers in the global agricultural market, as well as a finitude of important natural resources, such as phosphorus (P), this study tested the effect of the inoculation of rhizospheric or endophytic microorganisms isolated from Hymenaea courbaril and Butia purpurascens on the growth promotion of Glycine max (L.) Merr. The tests were conducted in a controlled greenhouse system, and the effects of biofertilization were evaluated using the following parameters: dry biomass, nutritional content, and photochemical and photosynthetic performance of plants. Seed biopriming was performed with four bacterial and four fungal isolates, and the results were compared to those of seeds treated with the commercial product Biomaphos®. Overall, microbial inoculation had a positive effect on biomass accumulation in G. max, especially in strains PA12 (Paenibacillus alvei), SC5 (Bacillus cereus), and SC15 (Penicillium sheari). The non-inoculated control plants accumulated less nutrients, both in the whole plant and aerial part, and had reduced chlorophyll index and low photosynthetic rate (A) and photochemical efficiency. Strains PA12 (P. alvei), SC5 (B. cereus), and 328EF (Codinaeopsis sp.) stood out in the optimization of nutrient concentration, transpiration rate, and stomatal conductance. Plants inoculated with the bacterial strains PA12 (P. alvei) and SC5 (B. cereus) and with the fungal strains 328EF (Codinaeopsis sp.) and SC15 (P. sheari) showed the closest pattern to that observed in plants treated with Biomaphos®, with the same trend of direction of the means associated with chlorophyll index, (A), dry mass, and concentration of important nutrients such as N, P, and Mg. We recommend the use of these isolates in field tests to validate these strains for the production of biological inoculants as part of the portfolio of bioinputs available for G. max.
Keywords: bioinputs; endophytic; plant growth promotion; plant mineral nutrition; rhizospheric.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Endophytic Fungi Inoculation Reduces Ramulosis Severity in Gossypium hirsutum Plants.Microorganisms. 2024 May 31;12(6):1124. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12061124. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38930506 Free PMC article.
-
Efficiency of the Hydroponic System as an Approach to Confirm the Solubilization of CaHPO4 by Microbial Strains Using Glycine max as a Model.Front Plant Sci. 2021 Oct 29;12:759463. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2021.759463. eCollection 2021. Front Plant Sci. 2021. PMID: 34777440 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Rhizobacteria Inoculation via Soil and Seeds on Glycine max L. Plants Grown on Soils with Different Cropping History.Microorganisms. 2022 Mar 23;10(4):691. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10040691. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 35456743 Free PMC article.
-
Multifunctional potential of endophytic and rhizospheric microbial isolates associated with Butia purpurascens roots for promoting plant growth.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2018 Nov;111(11):2157-2174. doi: 10.1007/s10482-018-1108-7. Epub 2018 May 30. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2018. PMID: 29850967
-
Grain Legume Yield Responses to Rhizobia Inoculants and Phosphorus Supplementation Under Ghana Soils: A Meta-Synthesis.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jun 23;13:877433. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.877433. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35812914 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Moisture content and mycorrhizal fungi in maternal environment influence performance and composition of Lallemantia species offspring.Heliyon. 2024 May 18;10(10):e31334. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31334. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38818147 Free PMC article.
-
Employing a Plant Probiotic Actinomycete for Growth Promotion of Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L. var. longifolia) Cultivated in a Hydroponic System under Nutrient Limitation.Plants (Basel). 2023 Nov 7;12(22):3793. doi: 10.3390/plants12223793. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38005691 Free PMC article.
-
The role of chemical fertilizer reduction and different microbial inoculants on yield increase in lettuce cultivation.BMC Plant Biol. 2025 Jul 29;25(1):981. doi: 10.1186/s12870-025-06986-w. BMC Plant Biol. 2025. PMID: 40730962 Free PMC article.
-
Endophytic Fungi Inoculation Reduces Ramulosis Severity in Gossypium hirsutum Plants.Microorganisms. 2024 May 31;12(6):1124. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12061124. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 38930506 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Effect of the Potassium Dose and Plant Biofertilization by Acinetobacter calcoaceticus on the Growth, Mineral Content, Nutritional Quality, Antioxidant Activity, and Metabolomic Features of Tomatillo Fruits (Physalis ixocarpa Brot.).Plants (Basel). 2023 Jan 19;12(3):466. doi: 10.3390/plants12030466. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36771548 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gawęda D., Nowak A., Haliniarz M., Woźniak A. Yield and economic effectiveness of soybean grown under different cropping systems. Int. J. Plant Prod. 2020;14:475–485. doi: 10.1007/s42106-020-00098-1. - DOI
-
- Meng X., Chen W.W., Wang Y.Y., Huang Z.R., Ye X., Chen L.S., Yang L.T. Effects of phosphorus deficiency on the absorption of mineral nutrients, photosynthetic system performance and antioxidant metabolism in Citrus grandis. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:e0246944. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0246944. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Henry J.B., Perkins-Veazie P., McCall I., Whipker B.E. Restricted phosphorus fertilization increases the betacyanin concentration and red foliage coloration of alternanthera. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2019;144:264–273. doi: 10.21273/JASHS04702-19. - DOI
-
- Reddy V.R., Cunha D.G.F., Kurian M. A water-energy-food nexus perspective on the challenge of eutrophication. Water. 2018;10:101. doi: 10.3390/w10020101. - DOI
-
- Edwards C.L., Maguire R.O., Alley M.M., Thomason W.E., Whitehurst G.B. Plant-available phosphorus after application of synthetic chelating agents. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2016;47:433–446. doi: 10.1080/00103624.2015.1122796. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

