Photothermal-Driven Liquid Crystal Elastomers: Materials, Alignment and Applications
- PMID: 35889204
- PMCID: PMC9317631
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27144330
Photothermal-Driven Liquid Crystal Elastomers: Materials, Alignment and Applications
Abstract
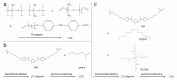
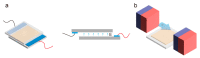
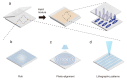
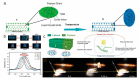
Liquid crystal elastomers (LCEs) are programmable deformable materials that can respond to physical fields such as light, heat, and electricity. Photothermal-driven LCE has the advantages of accuracy and remote control and avoids the requirement of high photon energy for photochemistry. In this review, we discuss recent advances in photothermal LCE materials and investigate methods for mechanical alignment, external field alignment, and surface-induced alignment. Advances in the synthesis and orientation of LCEs have enabled liquid crystal elastomers to meet applications in optics, robotics, and more. The review concludes with a discussion of current challenges and research opportunities.
Keywords: actuator; liquid crystal elastomer; smart material; soft robot.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






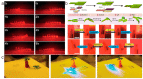



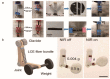
References
-
- De Gennes P.G. Possibilites Offertes par la Reticulation de Polymeres en Presence D’un Cristal Liquide. Phys. Lett. A. 1969;28:725–726. doi: 10.1016/0375-9601(69)90584-2. - DOI
-
- Thomsen D.L., Keller P., Naciri J., Pink R., Jeon H., Shenoy D., Ratna B.R. Liquid Crystal Elastomers with Mechanical Properties of a Muscle. Macromolecules. 2001;34:5868–5875. doi: 10.1021/ma001639q. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

