Allostery Inhibition of BACE1 by Psychotic and Meroterpenoid Drugs in Alzheimer's Disease Therapy
- PMID: 35889246
- PMCID: PMC9320338
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27144372
Allostery Inhibition of BACE1 by Psychotic and Meroterpenoid Drugs in Alzheimer's Disease Therapy
Abstract
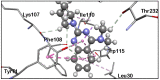
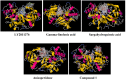
In over a century since its discovery, Alzheimer's disease (AD) has continued to be a global health concern due to its incurable nature and overwhelming increase among older people. In this paper, we give an overview of the efforts of researchers towards identifying potent BACE1 exosite-binding antibodies and allosteric inhibitors. Herein, we apply computer-aided drug design (CADD) methods to unravel the interactions of some proposed psychotic and meroterpenoid BACE1 allosteric site inhibitors. This study is aimed at validating the allosteric potentials of these selected compounds targeted at BACE1 inhibition. Molecular docking, molecular dynamic (MD) simulations, and post-MD analyses are carried out on these selected compounds, which have been experimentally proven to exhibit allosteric inhibition on BACE1. The SwissDock software enabled us to identify more than five druggable pockets on the BACE1 structural surface using docking. Besides the active site region, a melatonin derivative (compound 1) previously proposed as a BACE1 allostery inhibitor showed appreciable stability at eight different subsites on BACE1. Refinement with molecular dynamic (MD) simulations shows that the identified non-catalytic sites are potential allostery sites for compound 1. The allostery and binding mechanism of the selected potent inhibitors show that the smaller the molecule, the easier the attachment to several enzyme regions. This finding hereby establishes that most of these selected compounds failed to exhibit strong allosteric binding with BACE1 except for compound 1. We hereby suggest that further studies and additional identification/validation of other BACE1 allosteric compounds be done. Furthermore, this additional allosteric site investigation will help in reducing the associated challenges with designing BACE1 inhibitors while exploring the opportunities in the design of allosteric BACE1 inhibitors.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; BACE1; allosteric inhibitor; molecular docking; molecular dynamics (MD) simulations; multisite targeting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Alzheimer's Disease and β-secretase Inhibition: An Update with a Focus on Computer-aided Inhibitor Design.Curr Drug Targets. 2022;23(3):266-285. doi: 10.2174/1389450122666210809100050. Curr Drug Targets. 2022. PMID: 34370634 Review.
-
Identifying β-secretase 1 (BACE1) inhibitors from plant-based compounds: an approach targeting Alzheimer's therapeutics employing molecular docking and dynamics simulation.Mol Divers. 2024 Oct;28(5):2967-2980. doi: 10.1007/s11030-023-10726-3. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Mol Divers. 2024. PMID: 37728805
-
Computational modelling of potent β-secretase (BACE1) inhibitors towards Alzheimer's disease treatment.Biophys Chem. 2021 Mar;270:106536. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2020.106536. Epub 2020 Dec 26. Biophys Chem. 2021. PMID: 33387910
-
Identification of new BACE1 inhibitors for treating Alzheimer's disease.J Mol Model. 2021 Jan 30;27(2):58. doi: 10.1007/s00894-021-04679-3. J Mol Model. 2021. PMID: 33517514
-
An Overview of β-Amyloid Cleaving Enzyme 1 (BACE1) in Alzheimer's Disease Therapy: Elucidating its Exosite-Binding Antibody and Allosteric Inhibitor.Curr Med Chem. 2022;29(1):114-135. doi: 10.2174/0929867328666210608145357. Curr Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 34102967 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis and Evaluation of Chloride-Substituted Ramalin Derivatives for Alzheimer's Disease Treatment.Molecules. 2024 Aug 5;29(15):3701. doi: 10.3390/molecules29153701. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39125105 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing the Potential Contribution of In Silico Studies in Discovering Drug Candidates That Interact with Various SARS-CoV-2 Receptors.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 24;24(21):15518. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115518. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unveiling the Inhibitory Potentials of Peptidomimetic Azanitriles and Pyridyl Esters towards SARS-CoV-2 Main Protease: A Molecular Modelling Investigation.Molecules. 2023 Mar 14;28(6):2641. doi: 10.3390/molecules28062641. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36985614 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Peptidase Activity beyond the Active Site in Human Health and Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 4;24(23):17120. doi: 10.3390/ijms242317120. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069440 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

