Synthesis and Biological Activity Screening of Newly Synthesized Trimethoxyphenyl-Based Analogues as Potential Anticancer Agents
- PMID: 35889493
- PMCID: PMC9322052
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27144621
Synthesis and Biological Activity Screening of Newly Synthesized Trimethoxyphenyl-Based Analogues as Potential Anticancer Agents
Abstract
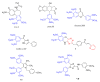
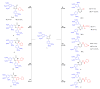
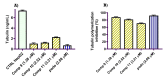
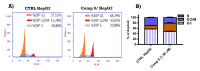
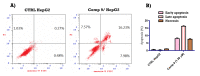
A group of novel trimethoxyphenyl (TMP)-based analogues were synthesized by varying the azalactone ring of 2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzylidene)oxazolone 1 and characterized using NMR spectral data as well as elemental microanalyses. All synthesized compounds were screened for their cytotoxic activity utilizing the hepatocellular carcinoma (HepG2) cell line. Compounds 9, 10 and 11 exhibited good cytotoxic potency with IC50 values ranging from 1.38 to 3.21 μM compared to podophyllotoxin (podo) as a reference compound. In addition, compounds 9, 10 and 11 exhibited potent inhibition of β-tubulin polymerization. DNA flow cytometry analysis of compound 9 shows cell cycle disturbance at the G2/M phase and a significant increase in Annexin-V-positive cells compared with the untreated control. Compound 9 was further studied regarding its apoptotic potential in HepG2 cells; it decreased the level of MMP and Bcl-2 as well as boosted the level of p53 and Bax compared with the control HepG2 cells.
Keywords: apoptosis; cell cycle analysis; cytotoxicity; diamide; imidazolone; oxazolone; triazinone; tubulin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel benzo[c]acridine-diones as potential anticancer agents and tubulin polymerization inhibitors.Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2019 Jun;352(6):e1800307. doi: 10.1002/ardp.201800307. Epub 2019 Apr 23. Arch Pharm (Weinheim). 2019. PMID: 31012156
-
Synthesis and Preclinical Evaluation of Indole Triazole Conjugates as Microtubule Targeting Agents that are Effective against MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cell Lines.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021;21(8):1047-1055. doi: 10.2174/1871520620666200925102940. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 32981511
-
Design, Synthesis and Cytotoxic Activity Evaluation of Newly Synthesized Amides-Based TMP Moiety as Potential Anticancer Agents over HepG2 Cells.Molecules. 2022 Jun 20;27(12):3960. doi: 10.3390/molecules27123960. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35745081 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of a terphenyl substituted 4-aza-2,3-didehydropodophyllotoxin analogues as inhibitors of tubulin polymerization and apoptosis inducers.Bioorg Med Chem. 2014 May 1;22(9):2714-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2014.03.021. Epub 2014 Mar 22. Bioorg Med Chem. 2014. PMID: 24721832
-
Investigation of podophyllotoxin esters as potential anticancer agents: synthesis, biological studies and tubulin inhibition properties.Eur J Med Chem. 2015 Jan 7;89:128-37. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.10.050. Epub 2014 Oct 18. Eur J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25462233
Cited by
-
New Heterocyclic Compounds from Oxazol-5(4H)-one and 1,2,4-Triazin-6(5H)-one Classes: Synthesis, Characterization and Toxicity Evaluation.Molecules. 2023 Jun 17;28(12):4834. doi: 10.3390/molecules28124834. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37375389 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Acrylate-Based Derivatives: Design, Synthesis, Antiproliferative Screening, and Docking Study as Potential Combretastatin Analogues.ACS Omega. 2023 Oct 9;8(41):38394-38405. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c05051. eCollection 2023 Oct 17. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37867686 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and cytotoxic research of a novel antitumor model based on acrylamide-PABA analogs via β-tubulin inhibition.RSC Adv. 2025 Jun 3;15(23):18490-18500. doi: 10.1039/d5ra02384j. eCollection 2025 May 29. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40463339 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bukhari S.N., Zakaria M.Y., Munir M.U., Ahmad N., Elsherif M.A., Badr R.E., Hassan A.K., Almaaty A.H.A., Zaki I. Design, Synthesis, In Vitro Biological Activity Evaluation and Stabilized Nanostructured Lipid Carrier Formulation of Newly Synthesized Schiff Bases-Based TMP Moieties. Pharmaceuticals. 2022;15:679. doi: 10.3390/ph15060679. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mielgo-Rubio X., Martín M., Remon J., Higuera O., Calvo V., Jarabo J.R., Conde E., Luna J., Provencio M., de Castro J., et al. Targeted therapy moves to earlier stages of non-small-cell lung cancer: Emerging evidence, controversies and future challenges. Future Oncol. 2021;17:4011–4025. doi: 10.2217/fon-2020-1255. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

