Stereoselective Processes Based on σ-Hole Interactions
- PMID: 35889497
- PMCID: PMC9323542
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27144625
Stereoselective Processes Based on σ-Hole Interactions
Abstract
The σ-hole interaction represents a noncovalent interaction between atoms with σ-hole(s) on their surface (such as halogens and chalcogens) and negative sites. Over the last decade, significant developments have emerged in applications where the σ-hole interaction was demonstrated to play a key role in the control over chirality. The aim of this review is to give a comprehensive overview of the current advancements in the use of σ-hole interactions in stereoselective processes, such as formation of chiral supramolecular assemblies, separation of enantiomers, enantioselective complexation and asymmetric catalysis.
Keywords: chalcogen bond; enantioselectivity; enantioseparation; halogen bond; noncovalent interaction; organocatalysis; recognition; σ-hole.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




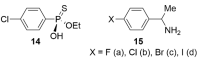



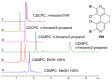









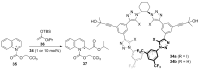

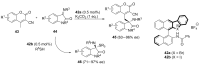
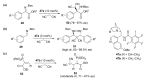
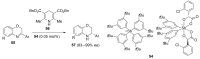
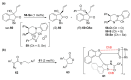
References
-
- Brinck T., Murray J.S., Politzer P. Surface Electrostatic Potentials of Halogenated Methanes as Indicators of Directional Intermolecular Interactions. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 1992;44:57–64. doi: 10.1002/qua.560440709. - DOI
-
- Desiraju G.R., Ho P.S., Kloo L., Legon A.C., Marquardt R., Metrangolo P., Politzer P., Resnati G., Rissanen K. Definition of the Halogen Bond (IUPAC Recommendations 2013) Pure Appl. Chem. 2013;85:1711–1713. doi: 10.1351/PAC-REC-12-05-10. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

