Nanotechnology-Based siRNA Delivery Systems to Overcome Tumor Immune Evasion in Cancer Immunotherapy
- PMID: 35890239
- PMCID: PMC9315482
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14071344
Nanotechnology-Based siRNA Delivery Systems to Overcome Tumor Immune Evasion in Cancer Immunotherapy
Abstract
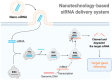
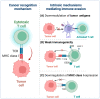
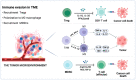
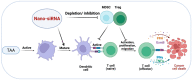
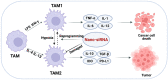
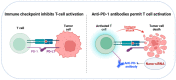
Immune evasion is a common reason causing the failure of anticancer immune therapy. Small interfering RNA (siRNA), which can activate the innate and adaptive immune system responses by silencing immune-relevant genes, have been demonstrated to be a powerful tool for preventing or reversing immune evasion. However, siRNAs show poor stability in biological fluids and cannot efficiently cross cell membranes. Nanotechnology has shown great potential for intracellular siRNA delivery in recent years. Nano-immunotherapy can efficiently penetrate the tumor microenvironment (TME) and deliver multiple immunomodulatory agents simultaneously, which appears to be a promising method for combination therapy. Therefore, it provides a new perspective for siRNA delivery in immunomodulation and cancer immunotherapy. The current advances and challenges in nanotechnology-based siRNA delivery strategies for overcoming immune evasion will be discussed in this review. In addition, we also offer insights into therapeutic options, which may expand its applications in clinical cancer treatment.
Keywords: immune evasion; immunotherapy; nanoparticles; small interfering RNA; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Gotwals P., Cameron S., Cipolletta D., Cremasco V., Crystal A., Hewes B., Mueller B., Quaratino S., Sabatos-Peyton C., Petruzzelli L., et al. Prospects for combining targeted and conventional cancer therapy with immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2017;17:286–301. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2017.17. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

