Effects of Drug-Free Pectin Hydrogel Films on Thermal Burn Wounds in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
- PMID: 35890648
- PMCID: PMC9316922
- DOI: 10.3390/polym14142873
Effects of Drug-Free Pectin Hydrogel Films on Thermal Burn Wounds in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
Abstract
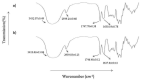
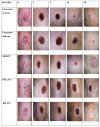
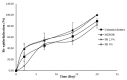
This study aims to examine the influence of drug-free pectin hydrogel films on partial-thickness burn wounds using streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats as the animal model. Thirty male Sprague Dawley rats were included in the wound healing study, and scalding water was used to produce wounds in the dorsum region of the rats. Two different formulations of pectin hydrogel films, PH 2.5% and PH 5%, were prepared using a solvent evaporation method. MEBO® (moist exposed burn ointment), a commercial herbal formulation was used as a positive control. The progress of the wound healing was observed and compared between untreated normal rats, untreated diabetic rats, diabetic rats treated with MEBO®, diabetic rats treated with PH 2.5%, and diabetic rats treated with PH 5%. The results showed that diabetic rats treated with PH 5% healed faster than the untreated diabetic rats and diabetic rats treated with PH 2.5%. Interestingly, the diabetic rats treated with PH 5% healed as well as diabetic rats treated with MEBO®, where wounds were healed entirely on day 20. Nevertheless, both PH 2.5% and PH 5% showed a greater zone of inhibition than MEBO® when tested against Staphylococcus aureus.
Keywords: diabetic rats; drug-free; hydrogel; pectin; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A Comparative Study of the Wound Healing Properties of Moist Exposed Burn Ointment (MEBO) and Silver Sulphadiazine.Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 2009 Jun 30;22(2):79-82. Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 2009. PMID: 21991159 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Moist Exposed Burn Therapy and Ointment (MEBT/MEBO) on the autophagy mTOR signalling pathway in diabetic ulcer wounds.Pharm Biol. 2020 Dec;58(1):124-130. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2019.1711430. Pharm Biol. 2020. PMID: 31967912 Free PMC article.
-
Moist exposed burn ointment accelerates diabetes-related wound healing by promoting re-epithelialization.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 10;9:1042015. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1042015. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36703885 Free PMC article.
-
The use of moist exposed burn ointment (MEBO) for the treatment of burn wounds: a systematic review.J Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2020 Dec;54(6):337-343. doi: 10.1080/2000656X.2020.1813148. Epub 2020 Sep 2. J Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2020. PMID: 32876517
-
Analysis of microbial environment changes in wound healing of pressure ulcers in rats promoted by moist exposed burn ointment.Arch Dermatol Res. 2025 Feb 22;317(1):451. doi: 10.1007/s00403-025-03913-9. Arch Dermatol Res. 2025. PMID: 39985596
Cited by
-
Impact of Crosslinking on the Characteristics of Pectin Monolith Cryogels.Polymers (Basel). 2022 Dec 1;14(23):5252. doi: 10.3390/polym14235252. Polymers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36501645 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the Biological Activity of Manna Exudate, from Fraxinus ornus L., and Its Potential Use as Hydrogel Formulation in Dermatology and Cosmetology.Gels. 2024 May 21;10(6):351. doi: 10.3390/gels10060351. Gels. 2024. PMID: 38920898 Free PMC article.
-
Natural and Synthetic Polymers for Biomedical and Environmental Applications.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Apr 20;16(8):1159. doi: 10.3390/polym16081159. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675078 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- IDF Diabetes Atlas 2021. 10th ed. International Diabetes Federation; Brussels, Belgium: 2022. [(accessed on 28 April 2022)]. Available online: https://www.diabetesatlas.org.
-
- Ahmed E.T., Abo-Salem O.M., Osman A. The Influence of Egyptian Propolis on Induced Burn Wound Healing in Diabetic Rats Antibacterial Mechanism. EWMA J. 2011;11:21–25.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

