Permutation-Based Block Code for Short Packet Communication Systems
- PMID: 35891069
- PMCID: PMC9323508
- DOI: 10.3390/s22145391
Permutation-Based Block Code for Short Packet Communication Systems
Abstract
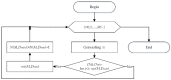
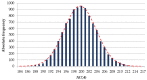
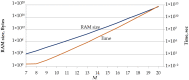
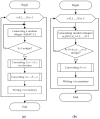
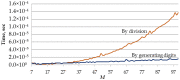
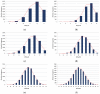
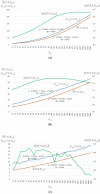
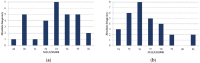
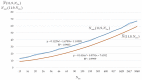
This paper presents an approach to the construction of block error-correcting code for data transmission systems with short packets. The need for this is driven by the necessity of information interaction between objects of machine-type communication network with a dynamically changing structure and unique system of commands or alerts for each network object. The codewords of a code are permutations with a given minimum pairwise Hamming distance. The purpose of the study is to develop a statistical method for constructing a code, in contrast to known algebraic methods, and to investigate the code size. An algorithm for generating codewords has been developed. It can be implemented both by enumeration of the full set of permutations, and by enumeration of a given number of randomly selected permutations. We have experimentally determined the dependencies of the average and the maximum values of the code size on the size of a subset of permutations used for constructing the code. A technique for computing approximation quadratic polynomials for the determined code size dependencies has been developed. These polynomials and their corresponding curves estimate the size of a code generated from a subset of random permutations of such a size that a statistically significant experiment cannot be performed. The results of implementing the developed technique for constructing a code based on permutations of lengths 7 and 11 have been presented. The prediction relative error of the code size did not exceed the value of 0.72% for permutation length 11, code distance 9, random permutation subset size 50,000, and permutation statistical study range limited by 5040.
Keywords: block error-correcting code; code size; codeword; factorial code; permutation; permutation code; secure channel coding scheme.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Statista Research Department Volume of Data/Information Created, Captured, Copied, and Consumed Worldwide from 2010 to 2025. [(accessed on 22 June 2022)]. Available online: https://www.statista.com/statistics/871513/worldwide-data-created/
-
- Avizienis A., Laprie J.-C., Randell B. Fundamental Concepts of Dependability. Department of Computing Science, University of Newcastle upon Tyne; Newcastle upon Tyne, UK: 2001. p. 21. (Department of Computing Science Technical Report Series).
-
- Durisi D., Liva G., Polyanskiy Y. Short-Packet Transmission. In: Marić I., Shamai (Shitz) S., Simeone O., editors. Information Theoretic Perspectives on 5G Systems and Beyond. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge, UK: 2022.
-
- Mahmood N.H., Böcker S., Moerman I., López O.A., Munari A., Mikhaylov K., Clazzer F., Bartz H., Park O.-S., Mercier E., et al. Machine Type Communications: Key Drivers and Enablers towards the 6G Era. J. Wirel. Com. Netw. 2021;2021:134. doi: 10.1186/s13638-021-02010-5. - DOI
-
- Elhoseny M., Hassanien A.E. Studies in Systems, Decision and Control. 1st ed. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2019. Dynamic Wireless Sensor Networks: New Directions for Smart Technologies.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

