Targeted Therapy of HPV Positive and Negative Tonsillar Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines Reveals Synergy between CDK4/6, PI3K and Sometimes FGFR Inhibitors, but Rarely between PARP and WEE1 Inhibitors
- PMID: 35891353
- PMCID: PMC9320646
- DOI: 10.3390/v14071372
Targeted Therapy of HPV Positive and Negative Tonsillar Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Lines Reveals Synergy between CDK4/6, PI3K and Sometimes FGFR Inhibitors, but Rarely between PARP and WEE1 Inhibitors
Abstract
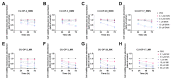
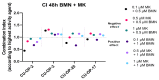
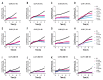
Human papillomavirus positive (HPV+) tonsillar and base of tongue squamous cell carcinoma (TSCC/BOTSCC) have a favorable outcome, but upon relapse, survival is poor and new therapeutical options are needed. Recently, we found synergistic effects by combining the food and drug administration approved (FDA) phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and fibroblast-growth-factor-receptor (FGFR) inhibitors BYL719 and JNJ-42756493 on TSCC cell lines. Here this approach was extended and Cyclin-Dependent-Kinase-4/6 (CDK4/6) and Poly-ADP-ribose-polymerase (PARP) and WEE1 inhibitors PD-0332991, and MK-1775 respectively were also examined. HPV+ CU-OP-2, -3, -20, and HPV- CU-OP-17 TSCC cell lines were treated with either BYL719 and JNJ-42756493, PD-0332991 BMN-673 and MK-1775 alone or in different combinations. Viability, proliferation, and cytotoxicity were followed by WST-1 assays and the IncuCyte S3 Live® Cell Analysis System. All inhibitors presented dose-dependent inhibitory effects on tested TSCC lines. Synergy was frequently obtained when combining CDK4/6 with PI3K inhibitors, but only sometimes or rarely when combining CDK4/6 with FGFR inhibitors or PARP with WEE1 inhibitors. To conclude, using CDK4/6 with PI3K or FGFR inhibitors, especially PD-0332991 with BYL719 presented synergy and enhanced the decrease of viability considerably, while although dose dependent responses were obtained with PARP and WEE1 inhibitors (BMN-673 and MK-1775 resp.), synergy was rarely disclosed.
Keywords: CDK4/6; FGFR; HPV; PARP; PI3K; WEE1; base of tongue cancer; head neck cancer; oropharyngeal cancer; targeted therapy; tonsillar cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Dahlgren L., Dahlstrand H., Lindquist D., Högmo A., Björnestål L., Lindholm J., Lundberg B., Dalianis T., Munck-Wikland E. Human papillomavirus is more common in base of tongue than in mobile tongue cancer and is a favorable prognostic factor in base of tongue cancer patients. Int. J. Cancer. 2004;112:1015–1019. doi: 10.1002/ijc.20490. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lindquist D., Romanitan M., Hammarstedt-Nordenvall L., Näsman A., Dahlstrand H., Lindholm J., Onelöv L., Ramqvist T., Ye W., Munck-Wikland E., et al. Human papillomavirus is a favourable prognostic factor in tonsillar cancer and its oncogenic role is supported by the expression of E6 and E7. Mol. Oncol. 2007;1:350–355. doi: 10.1016/j.molonc.2007.08.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dahlstrand H., Näsman A., Romanitan M., Lindquist D., Ramqvist T., Dalianis T. Human papillomavirus accounts both for increased incidence and better prognosis in tonsillar cancer. Anticancer. Res. 2008;28:1133–1138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

