Chronic kidney disease, survival and graft-versus-host-disease-free/relapse-free survival in recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant
- PMID: 35892015
- PMCID: PMC9308100
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfac091
Chronic kidney disease, survival and graft-versus-host-disease-free/relapse-free survival in recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant
Abstract
Background: Advances in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) have increased patient survival, although substantial treatment-related toxicity remains, including chronic kidney disease (CKD). We assessed the association between CKD and survival and transplant-specific outcomes in HSCT recipients.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective study of all 408 adult patients with allogenic HSCT at Princess Margaret Cancer Centre (Toronto, Canada, 2015-18). We used logistic regression to identify risk factors for CKD at 1 year post-transplant. Associations between CKD at 1 year and overall survival, relapse-free survival, graft-versus-host-disease (GVHD)-free/relapse-free survival, relapse and transplant-related mortality were examined using extended time-varying Cox models. In a sensitivity analysis, we restricted the cohort to survivors at 1 year, using standard Cox proportional hazard models to examine associations between CKD and overall survival, relapse-free survival and GVHD-free/relapse-free survival, and Fine and Gray's competing risk models to determine associations between CKD and relapse/transplant-related mortality.
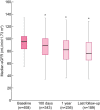
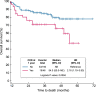
Results: The prevalence of CKD at 1 year was 19% (46 patients) with median follow-up of 23 months. Multivariable regression identified age at transplant [adjusted OR (aOR) 1.09, 95% confidence interval (95% CI) = 1.05-1.14; P < 0.0001), female gender (aOR 2.83, 95% CI = 1.34-5.97; P = 0.006) and acute kidney injury during the first 100 days (aOR 3.86, 95% CI = 1.70-8.73; P = 0.001) as risk factors for CKD at 1 year. Patients with CKD at 1 year had significantly poorer overall survival than those without CKD, when adjusted for relevant covariates [adjusted HR (aHR) 1.93, 95% CI = 1.02-3.66; P = 0.04 in the time-varying Cox model, and aHR 2.06, 95% CI = 1.04-4.07; P = 0.04 using the standard Cox model]. CKD at 1 year was also associated with worse GVHD-free/relapse-free survival (aHR 1.65, 95% CI = 1.04-2.61; P = 0.03).
Conclusions: CKD adversely affects the long-term prognosis for allogeneic HSCT recipients, with increased mortality risk and worse GVHD-free/relapse-free survival.
Keywords: GVHD-free/relapse-free survival; allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant; chronic kidney disease; long-term survival.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-term outcomes after standard graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis with or without anti-human-T-lymphocyte immunoglobulin in haemopoietic cell transplantation from matched unrelated donors: final results of a randomised controlled trial.Lancet Haematol. 2017 Jun;4(6):e293-e301. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(17)30081-9. Lancet Haematol. 2017. PMID: 28583289 Clinical Trial.
-
Risk of Subsequent Vitiligo in Transplant Recipients With Comorbid Graft-vs-Host Disease.JAMA Dermatol. 2024 Feb 1;160(2):194-198. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2023.4933. JAMA Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38091023 Free PMC article.
-
Who Is a Better Donor for Recipients of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: A Young HLA-Mismatched Haploidentical Relative or an Older Fully HLA-Matched Sibling or Unrelated Donor?Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019 Oct;25(10):2054-2060. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2019.05.031. Epub 2019 Jun 4. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019. PMID: 31173900
-
Haploidentical Transplantation with Post-Transplant Cyclophosphamide versus Unrelated Donor Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019 Dec;25(12):2422-2430. doi: 10.1016/j.bbmt.2019.07.028. Epub 2019 Aug 3. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019. PMID: 31386903
-
Alloreactivity as therapeutic principle in the treatment of hematologic malignancies. Studies of clinical and immunologic aspects of allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation with nonmyeloablative conditioning.Dan Med Bull. 2007 May;54(2):112-39. Dan Med Bull. 2007. PMID: 17521527 Review.
Cited by
-
Kidney Disease and Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation.Kidney360. 2025 Feb 1;6(2):317-330. doi: 10.34067/KID.0000000692. Epub 2025 Jan 9. Kidney360. 2025. PMID: 39786913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease in umbilical cord blood transplant recipients.Front Oncol. 2023 May 16;13:1186503. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1186503. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37260983 Free PMC article.
-
Incidence and risk factors for chronic kidney disease after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Ren Fail. 2025 Dec;47(1):2535517. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2025.2535517. Epub 2025 Aug 4. Ren Fail. 2025. PMID: 40755282 Free PMC article.
-
The prevalence of anemia in people with chronic kidney disease after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation.Ren Fail. 2023;45(2):2263581. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2023.2263581. Epub 2023 Oct 2. Ren Fail. 2023. PMID: 37782282 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

