Kidney function and the risk of sudden cardiac death in the general population
- PMID: 35892020
- PMCID: PMC9308098
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfac049
Kidney function and the risk of sudden cardiac death in the general population
Abstract
Background: Chronic kidney disease increases sudden cardiac death (SCD) risk, but the association between kidney function and SCD in a general population is largely unknown. Therefore, we investigated the association between kidney function and SCD in a general middle-aged and elderly population.
Methods: We included individuals aged ≥45 years from a prospective population-based cohort study. The association between kidney function assessments [estimated glomerular filtration rate based on serum creatinine (eGFRcreat), cystatin C (eGFRcys) or both (eGFRcreat-cys)] and SCD was investigated using Cox proportional-hazards and joint models. Absolute 10-year risks were computed using competing risk analyses. Mediation analyses were performed using a four-way decomposition method.
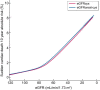
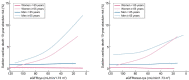
Results: We included 9687 participants (median follow-up 8.9 years; mean age 65.3 years; 56.7% women; 243 SCD cases). Lower eGFRcys and eGFRcreat-cys were associated with increased SCD risk [hazard ratio (HR) 1.23, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.12-1.34 and HR 1.17, 95% CI 1.06-1.29, per 10 mL/min/1.73 m2 eGFR decrease]. A significant trend (P = 0.001) across eGFRcys categories was found, with an HR of 2.11 (95% CI 1.19-3.74) for eGFRcys <60 compared with eGFRcys >90 mL/min/1.73 m2. Comparing eGFRcys of 90 to 60 mL/min/1.73 m2, absolute 10-year risk increased from 1.0% to 2.5%. Identified subgroups at increased risk included older participants and participants with atrial fibrillation. The associations were not mediated by coronary heart disease, hypertension or diabetes.
Conclusions: Reduced kidney function is associated with increased SCD risk in the general population, especially with eGFRcys. eGFRcys could be added to prediction models and screening programmes for SCD prevention.
Keywords: creatinine; cystatin C; estimated glomerular filtration rate; kidney function; sudden cardiac death.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Bidirectional Association Between Kidney Function and Atrial Fibrillation: A Population-Based Cohort Study.J Am Heart Assoc. 2022 May 17;11(10):e025303. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.122.025303. Epub 2022 May 17. J Am Heart Assoc. 2022. PMID: 35579615 Free PMC article.
-
Association between chronic kidney disease detected using creatinine and cystatin C and death and cardiovascular events in elderly Mexican Americans: the Sacramento Area Latino Study on Aging.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013 Jan;61(1):90-5. doi: 10.1111/jgs.12040. Epub 2012 Dec 18. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013. PMID: 23252993 Free PMC article.
-
Kidney function and sudden cardiac death in the community: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study.Am Heart J. 2016 Oct;180:46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2016.07.004. Epub 2016 Jul 14. Am Heart J. 2016. PMID: 27659882 Free PMC article.
-
Cystatin C-based estimated glomerular filtration rate and periodontitis.Gerodontology. 2016 Sep;33(3):328-34. doi: 10.1111/ger.12159. Epub 2014 Oct 8. Gerodontology. 2016. PMID: 25294234
-
[Clinical Importance of GFR-Estimating Equations (eGFRcreat and eGFRcys)].Rinsho Byori. 2015 Feb;63(2):259-64. Rinsho Byori. 2015. PMID: 26529980 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
The Decrease in Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate as a Risk Factor of Ventricular Tachyarrhythmias after Acute Myocardial Infarction during Hospitalization: A Retrospective Propensity Score Matching Cohort Study.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jan 29;25(2):42. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2502042. eCollection 2024 Feb. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39077336 Free PMC article.
-
A model study for the classification of high-risk groups for cardiac arrest in general ward patients using simulation techniques.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Sep 15;102(37):e35057. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035057. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37713881 Free PMC article.
-
Moderate Kidney Dysfunction Independently Increases Sudden Cardiac Arrest Risk: A Community-Based Study.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 13:2025.03.12.25323871. doi: 10.1101/2025.03.12.25323871. medRxiv. 2025. Update in: J Am Heart Assoc. 2025 Aug 5;14(15):e042307. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.125.042307. PMID: 40162277 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillators in Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death in Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Case Series and an Appraisal of Current Evidence.J Clin Med. 2024 Sep 29;13(19):5820. doi: 10.3390/jcm13195820. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39407880 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Sudden Cardiac Death: Looking Beyond Ejection Fraction.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2023 Jun;25(6):525-534. doi: 10.1007/s11886-023-01871-0. Epub 2023 Apr 10. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37036554 Review.
References
-
- Morin DP, Homoud MK, Estes NAM III. Prediction and prevention of sudden cardiac death. Card Electrophysiol Clin 2017; 9: 631–638 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

