Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensors with Magnetic Sandwich Hybrids for Signal Amplification
- PMID: 35892451
- PMCID: PMC9332597
- DOI: 10.3390/bios12080554
Surface Plasmon Resonance Biosensors with Magnetic Sandwich Hybrids for Signal Amplification
Abstract
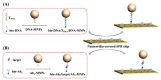
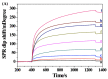
The conventional signal amplification strategies for surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensors involve the immobilization of receptors, the capture of target analytes and their recognition by signal reporters. Such strategies work at the expense of simplicity, rapidity and real-time measurement of SPR biosensors. Herein, we proposed a one-step, real-time method for the design of SPR biosensors by integrating magnetic preconcentration and separation. The target analytes were captured by the receptor-modified magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs), and then the biotinylated recognition elements were attached to the analyte-bound MNPs to form a sandwich structure. The sandwich hybrids were directly delivered to the neutravidin-modified SPR fluidic channel. The MNPs hybrids were captured by the chip through the neutravidin-biotin interaction, resulting in an enhanced SPR signal. Two SPR biosensors have been constructed for the detection of target DNA and beta-amyloid peptides with high sensitivity and selectivity. This work, integrating the advantages of one-step, real-time detection, multiple signal amplification and magnetic preconcentration, should be valuable for the detection of small molecules and ultra-low concentrations of analytes.
Keywords: biosensors; magnetic preconcentration; signal amplification; surface plasmon resonance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Magnetic nanoparticle enhanced surface plasmon resonance sensing and its application for the ultrasensitive detection of magnetic nanoparticle-enriched small molecules.Anal Chem. 2010 Aug 15;82(16):6782-9. doi: 10.1021/ac100812c. Anal Chem. 2010. PMID: 20704367
-
Fe3O4 nanoparticles-enhanced SPR sensing for ultrasensitive sandwich bio-assay.Talanta. 2011 May 15;84(3):783-8. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2011.02.020. Epub 2011 Feb 19. Talanta. 2011. PMID: 21482283
-
Ultrasensitive detection of deltamethrin by immune magnetic nanoparticles separation coupled with surface plasmon resonance sensor.Biosens Bioelectron. 2014 Sep 15;59:328-34. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2014.03.020. Epub 2014 Apr 13. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014. PMID: 24747571
-
Signal amplification strategies for DNA-based surface plasmon resonance biosensors.Biosens Bioelectron. 2018 Oct 15;117:678-689. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2018.06.062. Epub 2018 Jun 30. Biosens Bioelectron. 2018. PMID: 30007198 Review.
-
Strategies for Surface Design in Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) Sensing.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Apr 7;13(4):465. doi: 10.3390/bios13040465. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37185540 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Advancements in magnetic nanoparticle-based biosensors for point-of-care testing.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Apr 25;12:1393789. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1393789. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38725992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Label-Free Direct Detection of Cylindrospermopsin via Graphene-Enhanced Surface Plasmon Resonance Aptasensor.Toxins (Basel). 2023 May 10;15(5):326. doi: 10.3390/toxins15050326. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37235360 Free PMC article.
-
The Current Status and Future Promise of SPR Biosensors.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Oct 27;12(11):933. doi: 10.3390/bios12110933. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36354442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tabasi O., Falamaki C. Recent advancements in the methodologies applied for the sensitivity enhancement of surface plasmon resonance sensors. Anal. Methods. 2018;10:3906. doi: 10.1039/C8AY00948A. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

