A Systematic Review on the Effect of Nutraceuticals on Antidepressant-Induced Sexual Dysfunctions: From Basic Principles to Clinical Applications
- PMID: 35892716
- PMCID: PMC9332380
- DOI: 10.3390/cimb44080230
A Systematic Review on the Effect of Nutraceuticals on Antidepressant-Induced Sexual Dysfunctions: From Basic Principles to Clinical Applications
Abstract
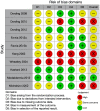
Sexual dysfunctions are common side effects reported by patients during antidepressant treatment. When they occur, patients often discontinue psychopharmacological therapy, with a negative impact on the underlying psychiatric disease. Recently, great attention has been paid to the use of nutraceuticals in the management of psychiatric disorders, although a systematic review on their effects as a treatment option for antidepressant-induced sexual dysfunctions (AISD) is lacking. Here, we conducted a systematic search in the following databases: MEDLINE (through PubMed), EMBASE, PsycINFO, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, and Web of Science. We searched eligible studies among parallel or crossover randomized controlled trials (RCTs) in adult populations. After this process, a total of 10 articles that evaluated the effect of six different nutraceuticals versus placebo were included: Maca Root, S-adenosyl-L-methionine (SAMe), Rosa Damascena, Ginkgo Biloba, Saffron, and Yohimbine. Overall, a high dose of Maca Root and the use of SAMe or Saffron may improve AISD. Additionally, the administration of Rosa Damascena seemed to be more effective in men than in women, whereas no evidence of effects emerged for Gingko Biloba and Yohimbine. Given the mixed results still available, future RCTs should consider larger samples and confounding factors, such as depressive status and individual vulnerability.
Keywords: antidepressants; depression; nutraceuticals; sexual dysfunctions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adjuvant therapy with antidepressants for the management of inflammatory bowel disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019 Apr 12;4(4):CD012680. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012680.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019. PMID: 30977111 Free PMC article.
-
A double-blind placebo-controlled trial of maca root as treatment for antidepressant-induced sexual dysfunction in women.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015;2015:949036. doi: 10.1155/2015/949036. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2015. PMID: 25954318 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review of clinical trials on Ginkgo (Ginkgo biloba) effectiveness on sexual function and its safety.Avicenna J Phytomed. 2021 Jul-Aug;11(4):324-331. doi: 10.22038/AJP.2021.17813. Avicenna J Phytomed. 2021. PMID: 34290964 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systematic reviews of the effectiveness of day care for people with severe mental disorders: (1) acute day hospital versus admission; (2) vocational rehabilitation; (3) day hospital versus outpatient care.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(21):1-75. doi: 10.3310/hta5210. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532238 Review.
-
Complementary and alternative medicine for major depressive disorder: a meta-analysis of patient characteristics, placebo-response rates, and treatment outcomes relative to standard antidepressants.J Clin Psychiatry. 2010 Jun;71(6):682-8. doi: 10.4088/JCP.10r05976blu. J Clin Psychiatry. 2010. PMID: 20573327
Cited by
-
Antidepressant-associated sexual dysfunction in outpatients.BMC Psychiatry. 2025 Apr 2;25(1):317. doi: 10.1186/s12888-025-06751-1. BMC Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40175958 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological treatment of antidepressant-induced sexual dysfunction in women: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2025 Feb 21;80:100602. doi: 10.1016/j.clinsp.2025.100602. eCollection 2025. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2025. PMID: 39985829 Free PMC article.
-
Not All Maca Is Created Equal: A Review of Colors, Nutrition, Phytochemicals, and Clinical Uses.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 14;16(4):530. doi: 10.3390/nu16040530. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38398854 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources