The Use of Sea Buckthorn Processing Products in the Creation of a Functional Biologically Active Food Emulsion
- PMID: 35892810
- PMCID: PMC9332202
- DOI: 10.3390/foods11152226
The Use of Sea Buckthorn Processing Products in the Creation of a Functional Biologically Active Food Emulsion
Abstract
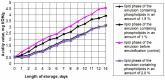
The current trend in dietary supplements and functional foods is the use of lipophilic bioactive compounds. The sea buckthorn (Hippóphae rhamnoídes) contains some such compounds: polyunsaturated fatty acids, tocopherols, and carotenoids. Lipophilic components are best distributed using oil-in-water emulsions, which ensures their high bioavailability. A significant property of emulsions is colloidal and oxidative stability, so the choice of emulsifiers that have both surface-active properties and antioxidant activity is an important area of research for making new types of food emulsions. The purpose of this study is the development and refinement of an emulsified biologically active food additive containing sea buckthorn products (pulp, juice, and oil) and stabilized with soy phospholipids. We studied the fruits of Chuyskaya, Orange, and Prevoskhodnaya sea buckthorn varieties growing in the Altai Territory. As we analyzed their composition, we chose the Chuyskaya variety for making the emulsion. The fruits contain 5.30 ± 0.1% of lipids including 16.8 ± 0.5 mg/100 g of carotenoids and 10.5 ± 0.5 mg/100 g of tocopherols. To choose the emulsifier we studied the fractional and fatty acid composition of the soy and sunflower phospholipids with different hydrophilic-lipophilic balances (HLB). We made the emulsions containing sea buckthorn oil and pulp of its different layers, soybean oil, and phospholipids by dispersion using an HG-15D homogenizer. The study of the colloidal stability showed that the most stable (99.5%) are the emulsions containing a mixture of hydrolyzed soybean phospholipids (HLB = 7) and fractionated soybean phospholipids (HLB = 3). The best ratio is 40:60. We examined the oxidative stability of the emulsions by provoking accelerated oxidation. The emulsions containing 1.5% of a soy phospholipids mixture showed the best oxidative stability. The resulting direct oil-in-water fine emulsion contains polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), tocopherols, β-carotene, and essential phospholipids. For this reason, the emulsion can be used to make biologically active food supplements (also encapsulated) and as part of special nutrients.
Keywords: carotenoids; colloidal stability; emulsifiers; emulsions; food additive; oxidative stability; phospholipids; sea buckthorn; sea buckthorn oil; tocopherols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Baboota R.K., Bishnoi M., Ambalam P., Kondepudi K.K., Sarma S.M., Boparai R.K., Podili K. Functional food ingredients for the management of obesity and associated co-morbidities—A review. J. Funct. Foods. 2013;5:997–1012. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2013.04.014. - DOI
-
- Bolori P., Setaysh L., Rasaei N., Jarrahi F., Yekaninejad M.S., Mirzaei K. Adherence to a healthy plant diet may reduce inflammatory factors in obese and overweight women—A cross-sectional study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. J. Clin. Res. Rev. 2019;13:2795–2802. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2019.07.019. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kovell L.C., Yeung E.H., Miller E.R., III, Appel L.J., Christenson R.H., Rebuck H., Schulman S.P., Juraschek S.P. Healthy diet reduces markers of cardiac injury and inflammation regardless of macronutrients: Results from the OmniHeart trial. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020;299:282–288. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2019.07.102. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials