Infective Endocarditis in High-Income Countries
- PMID: 35893249
- PMCID: PMC9329978
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo12080682
Infective Endocarditis in High-Income Countries
Abstract
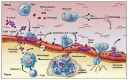
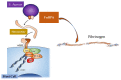
Infective endocarditis remains an illness that carries a significant burden to healthcare resources. In recent times, there has been a shift from Streptococcus sp. to Staphylococcus sp. as the primary organism of interest. This has significant consequences, given the virulence of Staphylococcus and its propensity to form a biofilm, rendering non-surgical therapy ineffective. In addition, antibiotic resistance has affected treatment of this organism. The cohorts at most risk for Staphylococcal endocarditis are elderly patients with multiple comorbidities. The innovation of transcatheter technologies alongside other cardiac interventions such as implantable devices has contributed to the increased risk attributable to this cohort. We examined the pathophysiology of infective endocarditis carefully. Inter alia, the determinants of Staphylococcus aureus virulence, interaction with host immunity, as well as the discovery and emergence of a potential vaccine, were investigated. Furthermore, the potential role of prophylactic antibiotics during dental procedures was also evaluated. As rates of transcatheter device implantation increase, endocarditis is expected to increase, especially in this high-risk group. A high level of suspicion is needed alongside early initiation of therapy and referral to the heart team to improve outcomes.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; biofilm; fibronectin; immune response; infective endocarditis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Murdoch D.R., Corey G.R., Hoen B., Miró J.M., Fowler V.G., Bayer A.S., Karchmer A.W., Olaison L., Pappas P.A., Moreillon P., et al. Clinical presentation, etiology, and outcome of infective endocarditis in the 21st century: The International Collaboration on Endocarditis-Prospective Cohort Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009;169:463–473. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2008.603. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liaqat W., Palaiodimos L., Li W., Karamanis D., Tahir A., Tzoumas A., Nagraj S., Tiwari N., Grushko M., Kokkinidis D., et al. Epidemiologic and clinical characteristics of infective endocarditis: A single-center retrospective study in the Bronx, New York. Infection. 2022:1–13. doi: 10.1007/s15010-022-01846-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Paul G., Ochs L., Hohmann C., Baldus S., Michels G., Meyer-Schwickerath C., Fätkenheuer G., Mader N., Wahlers T., Weber C., et al. Surgical Procedure Time and Mortality in Patients with Infective Endocarditis Caused by Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus Species. J. Clin. Med. 2022;11:2538. doi: 10.3390/jcm11092538. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Selton-Suty C., Célard M., Le Moing V., Doco-Lecompte T., Chirouze C., Iung B., Strady C., Revest M., Vandenesch F., Bouvet A. Preeminence of Staphylococcus aureus in infective endocarditis: A 1-year population-based survey. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012;54:1230–1239. doi: 10.1093/cid/cis199. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chen H., Zhan Y., Zhang K., Gao Y., Chen L., Zhan J., Chen Z., Zeng Z. The Global, Regional, and National Burden and Trends of Infective Endocarditis From 1990 to 2019: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Front. Med. 2022;9:774224. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.774224. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

