Improvement of Glycemic Control by a Functional Food Mixture Containing Maltodextrin, White Kidney Bean Extract, Mulberry Leaf Extract, and Niacin-Bound Chromium Complex in Obese Diabetic db/db Mice
- PMID: 35893259
- PMCID: PMC9394435
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo12080693
Improvement of Glycemic Control by a Functional Food Mixture Containing Maltodextrin, White Kidney Bean Extract, Mulberry Leaf Extract, and Niacin-Bound Chromium Complex in Obese Diabetic db/db Mice
Abstract
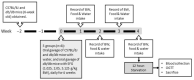
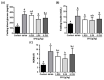
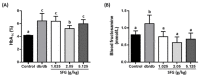
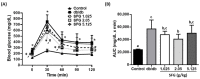
Steady-fiber granule (SFG) is a mixture containing maltodextrin, white kidney bean extract, mulberry leaf extract, and niacin-bound chromium complex. These active ingredients have been shown to be associated with improving either hyperglycemia or hyperlipidemia. This study was undertaken to evaluate the potential of SFG in the regulation of blood glucose homeostasis under obese diabetic conditions. Accordingly, db/db mice (8 weeks old) were administered with SFG at doses of 1.025, 2.05, or 5.125 g/kg BW daily via oral gavage for 4 weeks. No body weight loss was observed after SFG supplementation at all three doses during the experimental period. Supplementation of SFG at 2.05 g/kg BW decreased fasting blood glucose, blood fructosamine, and HbA1c levels in db/db mice. Insulin sensitivity was also improved, as indicated by HOMA-IR assessment and oral glucose tolerance test, although the fasting insulin levels were no different in db/db mice with or without SFG supplementation. Meanwhile, the plasma levels of triglyceride were reduced by SFG at all three doses. These findings suggest that SFG improves glycemic control and insulin sensitivity in db/db mice and can be available as an option for functional foods to aid in management of type 2 diabetes mellitus in daily life.
Keywords: functional foods; hyperglycemia; insulin resistance; steady-fiber granule; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genotoxicity and 28-day oral toxicity studies of a functional food mixture containing maltodextrin, white kidney bean extract, mulberry leaf extract, and niacin-bound chromium complex.Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2018 Feb;92:67-74. doi: 10.1016/j.yrtph.2017.11.008. Epub 2017 Nov 16. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29155076
-
Flavonoids extracted from mulberry (Morus alba L.) leaf improve skeletal muscle mitochondrial function by activating AMPK in type 2 diabetes.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Feb 10;248:112326. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112326. Epub 2019 Oct 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31639486
-
Anti-hyperglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of Cistanche tubulosa in type 2 diabetic db/db mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Dec 12;150(3):935-45. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.09.027. Epub 2013 Oct 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 24095831
-
Effects of dietary mulberry, Korean red ginseng, and banaba on glucose homeostasis in relation to PPAR-alpha, PPAR-gamma, and LPL mRNA expressions.Life Sci. 2005 Nov 12;77(26):3344-54. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2005.05.043. Epub 2005 Jun 23. Life Sci. 2005. PMID: 15979095
-
Red Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) Seed Extract Improves Glycemic Control by Inhibiting Hepatic Gluconeogenesis via Phosphorylation of FOXO1 and AMPK in Obese Diabetic db/db Mice.Nutrients. 2020 Aug 23;12(9):2546. doi: 10.3390/nu12092546. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32842462 Free PMC article.
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation . In: IDF Diabetes Atlas, 2017. 8th ed. Suvi K., Joao da Rocha Fernandes B.M., editors. International Diabetes Federation; Brussels, Belgium: 2017. [(accessed on 3 February 2020)]. Available online: http://www.diabetesatlas.org/
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Diabetes Statistics Report website. [(accessed on 9 May 2022)];2022 Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/data/statistics-report/index.html.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

