Bioinformatics Study of Aux/IAA Family Genes and Their Expression in Response to Different Hormones Treatments during Japanese Apricot Fruit Development and Ripening
- PMID: 35893602
- PMCID: PMC9332017
- DOI: 10.3390/plants11151898
Bioinformatics Study of Aux/IAA Family Genes and Their Expression in Response to Different Hormones Treatments during Japanese Apricot Fruit Development and Ripening
Abstract
Auxin/indole-3-acetic acid (Aux/IAA) is a transcriptional repressor in the auxin signaling pathway that plays a role in several plant growth and development as well as fruit and embryo development. However, it is unclear what role they play in Japanese apricot (Prunus mume) fruit development and maturity. To investigate the role of Aux/IAA genes in fruit texture, development, and maturity, we comprehensively identified and expressed 19 PmIAA genes, and demonstrated their conserved domains and homology across species. The majority of PmIAA genes are highly responsive and expressed in different hormone treatments. PmIAA2, PmIAA5, PmIAA7, PmIAA10, PmIAA13, PmIAA18, and PmIAA19 showed a substantial increase in expression, suggesting that these genes are involved in fruit growth and maturity. During fruit maturation, alteration in the expression of PmIAA genes in response to 1-Methylcyclopropene (1-MCP) treatment revealed an interaction between auxin and ethylene. The current study investigated the response of Aux/IAA development regulators to auxin during fruit ripening, with the goal of better understanding their potential application in functional genomics.
Keywords: Aux/IAA; Japanese apricot; fruit maturity; hormones.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




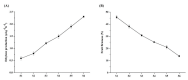
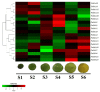
References
-
- Shi H., Wang Y., Li Z., Zhang D., Zhang Y., Xiang D., Li Y., Zhang Y. Pear IAA1 gene encoding an auxin-responsive Aux/IAA protein is involved in fruit development and response to salicylic acid. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2014;94:263–271. doi: 10.4141/cjps2013-290. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

