Reduction in Acquisition Time and Improvement in Image Quality in T2-Weighted MR Imaging of Musculoskeletal Tumors of the Extremities Using a Novel Deep Learning-Based Reconstruction Technique in a Turbo Spin Echo (TSE) Sequence
- PMID: 35894013
- PMCID: PMC9326558
- DOI: 10.3390/tomography8040148
Reduction in Acquisition Time and Improvement in Image Quality in T2-Weighted MR Imaging of Musculoskeletal Tumors of the Extremities Using a Novel Deep Learning-Based Reconstruction Technique in a Turbo Spin Echo (TSE) Sequence
Abstract
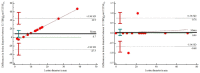
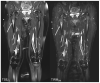
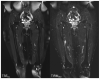
Background: The aim of this study was to assess the technical feasibility and the impact on image quality and acquisition time of a deep learning-accelerated fat-saturated T2-weighted turbo spin echo sequence in musculoskeletal imaging of the extremities. Methods: Twenty-three patients who underwent MRI of the extremities were prospectively included. Standard T2w turbo inversion recovery magnitude (TIRMStd) imaging was compared to a deep learning-accelerated T2w TSE (TSEDL) sequence. Image analysis of 23 patients with a mean age of 60 years (range 30−86) was performed regarding image quality, noise, sharpness, contrast, artifacts, lesion detectability and diagnostic confidence. Pathological findings were documented measuring the maximum diameter. Results: The analysis showed a significant improvement for the T2 TSEDL with regard to image quality, noise, contrast, sharpness, lesion detectability, and diagnostic confidence, as compared to T2 TIRMStd (each p < 0.001). There were no differences in the number of detected lesions. The time of acquisition (TA) could be reduced by 52−59%. Interrater agreement was almost perfect (κ = 0.886). Conclusion: Accelerated T2 TSEDL was technically feasible and superior to conventionally applied T2 TIRMStd. Concurrently, TA could be reduced by 52−59%. Therefore, deep learning-accelerated MR imaging is a promising and applicable method in musculoskeletal imaging.
Keywords: accelerated turbo spin echo MRI; artificial intelligence; deep learning; musculoskeletal imaging; musculoskeletal tumors.
Conflict of interest statement
Dominik Nickel is an employee of Siemens Healthcare. Siemens Healthcare is a financial partner of the Radiological Department of the University Hospital of Tübingen.
Figures


References
-
- Papworth K.E., Arroyo V.M., Styring E., Zaikova O., Melin B.S., Lupo P.J. Soft-tissue sarcoma in adolescents and young adults compared with older adults: A report among 5000 patients from the Scandinavian Sarcoma Group Central Register. Cancer. 2019;125:3595–3602. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32367. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

