Management of Anticoagulation during Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Children
- PMID: 35894028
- PMCID: PMC9326610
- DOI: 10.3390/pediatric14030039
Management of Anticoagulation during Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in Children
Abstract
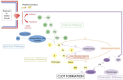
Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) is often used in critically ill children with severe cardiopulmonary failure. Worldwide, about 3600 children are supported by ECMO each year, with an increase of 10% in cases per year. Although anticoagulation is necessary to prevent circuit thrombosis during ECMO support, bleeding and thrombosis are associated with significantly increased mortality risk. In addition, maintaining balanced hemostasis is a challenging task during ECMO support. While heparin is a standard anticoagulation therapy in ECMO, recently, newer anticoagulant agents are also in use. Currently, there is a wide variation in anticoagulation management and diagnostic monitoring in children receiving ECMO. This review intends to describe the pathophysiology of coagulation during ECMO support, review of literature on current and newer anticoagulant agents, and outline various diagnostic tests used for anticoagulation monitoring. We will also discuss knowledge gaps and future areas of research.
Keywords: ECMO; anticoagulation; bleeding; children; extracorporeal life support; extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; thrombosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bowen F.W., Edmunds H.L. ECMO Extracorporeal Cardiopulmonary Support in Critical Care. ELSO; Ann Arbor, MI, USA: 2000. Coagulation, Anticoagulation and the Interaction of Blood and Artificial Surfaces; pp. 67–96.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources