Effects of liraglutide on gastrointestinal functions and weight in obesity: A randomized clinical and pharmacogenomic trial
- PMID: 35894080
- PMCID: PMC9335902
- DOI: 10.1002/oby.23481
Effects of liraglutide on gastrointestinal functions and weight in obesity: A randomized clinical and pharmacogenomic trial
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to determine the effects of a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, liraglutide, and placebo subcutaneously over 16 weeks on weight and gastric functions and to evaluate associations of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in GLP1R (rs6923761) and TCF7L2 (rs7903146) with effects of liraglutide.
Methods: The study conducted a randomized, parallel-group, placebo-controlled, 16-week trial of liraglutide, escalated to 3 mg subcutaneously daily in 136 otherwise healthy adults with obesity. Weight, gastric emptying of solids (GES), gastric volumes, satiation, and body composition measured at baseline and after treatment were compared in two treatment groups using analysis of covariance.
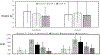
Results: Liraglutide (n = 59) and placebo (n = 65) groups completed treatment. Relative to placebo, liraglutide increased weight loss at 5 and 16 weeks (both p < 0.05), slowed time to half GES (T1/2 ) at 5 and 16 weeks (both p < 0.001), and increased fasting gastric volume (p = 0.01) and satiation (p < 0.01) at 16 weeks. GES T1/2 was positively correlated with weight loss on liraglutide (both p < 0.001). After 16 weeks of liraglutide, GLP1R rs6923761 (AG/AA vs. GG) was associated with reduced percent body fat (p = 0.062), and TCF7L2 rs7903146 (CC vs. CT/TT) was associated with lower body weight (p = 0.015).
Conclusions: Liraglutide, 3 mg, induces weight loss with delay in GES T1/2 and reduces calorie intake. Slowing GES and variations in GLP1R and TCF7L2 are associated with liraglutide effects in obesity.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02647944.
© 2022 The Obesity Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures:
A. Acosta is a stockholder in Gila Therapeutics, Phenomix Sciences and Lipiquester; he serves as a consultant for Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, General Mills, Gila Therapeutics.
M. Camilleri is a stockholder in Phenomix Sciences (with current shares valued at less than U.S.$1.00) and serves as a consultant to Kallyope (with consulting fee paid to his employer, Mayo Clinic).
The other authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



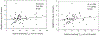
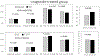
Comment in
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, weight loss, and gastric emptying: have I gut news for you.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2022 Aug;30(8):1533-1534. doi: 10.1002/oby.23525. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2022. PMID: 35894084 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Prevalence and variations in gastric emptying delay in response to GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2024 Feb;32(2):232-233. doi: 10.1002/oby.23941. Epub 2023 Nov 5. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2024. PMID: 37927173 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Maselli DB, Camilleri M. Effects of GLP-1 and its analogs on gastric physiology in diabetes mellitus and obesity. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1307:171–192. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

