Profiling vitamin D, its mediators and proinflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis: A case-control study
- PMID: 35894711
- PMCID: PMC9274797
- DOI: 10.1002/iid3.676
Profiling vitamin D, its mediators and proinflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis: A case-control study
Abstract
Introduction: The active form of vitamin D has immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effect. Vitamin D is implicated in pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and its deficiency leads to increased inflammation. Moreover, its production is dependent on concentration of calcium, phosphorus, and parathyroid hormone (PTH). Cytokines mediates inflammation in RA synovium. This study evaluated vitamin D, its mediators and proinflammatory cytokines among RA patients.
Methods: In a case-control study, 78 RA patients from Komfo Anokye Teaching Hospital rheumatology clinic and 60 healthy blood donors were recruited. Chemistry analyzer and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kits were used to measure biochemical parameters and cytokines.
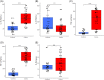
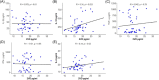
Results: We found significantly higher levels of interleukin (IL)-1β, interferon gamma (IFN-γ), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in RA patients compared with controls (p < .05). There was a significant positive correlation between intact parathyroid hormone (iPTH) and IL-10 (r = .30, p < .05) and a negative correlation between IL-6 (r = -0.28, p > .05), IL-1β (r = -0.25, p > .05), TNF-α (r = -0.26, p > .05), IFN-γ (r = -0.24, p > .05), and iPTH. There was a significant negative correlation between IL-1β (r = -0.33, p < .05), IFN- γ (r = -0.29, p < .05), and calcium.
Conclusion: Reduced PTH, calcium, and phosphorus is associated with higher levels of proinflammatory cytokines which may worsen RA disease condition. Vitamin D is therefore not an independent regulator of proinflammatory cytokines in RA.
Keywords: mediators of vitamin D; parathyroid hormone; phosphorus; proinflammatory cytokines; rheumatoid arthritis.
© 2022 The Authors. Immunity, Inflammation and Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Synovium as a source of increased amino-terminal parathyroid hormone-related protein expression in rheumatoid arthritis. A possible role for locally produced parathyroid hormone-related protein in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis.J Clin Invest. 1998 Apr 1;101(7):1362-71. doi: 10.1172/JCI484. J Clin Invest. 1998. PMID: 9525978 Free PMC article.
-
Mast cell activation and its relation to proinflammatory cytokine production in the rheumatoid lesion.Arthritis Res. 2000;2(1):65-74. doi: 10.1186/ar70. Arthritis Res. 2000. PMID: 11219391 Free PMC article.
-
Level of inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis patients: Correlation with 25-hydroxy vitamin D and reactive oxygen species.PLoS One. 2017 Jun 8;12(6):e0178879. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0178879. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28594861 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of receptor activator of NFkappaB ligand and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis.Bone. 2002 Feb;30(2):340-6. doi: 10.1016/s8756-3282(01)00682-2. Bone. 2002. PMID: 11856640 Review.
-
Pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis.Ann Med. 1997 Dec;29(6):499-507. doi: 10.3109/07853899709007474. Ann Med. 1997. PMID: 9562516 Review.
Cited by
-
The Magic Triangle in Oral Potentially Malignant Disorders: Vitamin D, Vitamin D Receptor, and Malignancy.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 11;24(20):15058. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015058. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Receptors expressions on peripheral lymphocytes and CD4+ CD183+ as a diagnostics biomarker for rheumatoid arthritis: A case-control study in Ghana.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Aug;11(8):e976. doi: 10.1002/iid3.976. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 37647423 Free PMC article.
-
Leucine-Rich Repeat Containing 15 Promotes the Inflammatory Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis by Regulating NF-κB Pathway.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2025 Jul;13(7):e70220. doi: 10.1002/iid3.70220. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2025. PMID: 40642947 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-21 correlates with the reactive oxygen species and 25-hydroxy vitamin D in rheumatoid arthritis patients.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024 Jul;12(7):e1308. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1308. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2024. PMID: 39056553 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling the link between chronic inflammation and primary hyperparathyroidism: a systematic review.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 2;16:1563967. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1563967. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40529359 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cooles FA, Isaacs JD. Pathophysiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011;23(3):233‐240. - PubMed
-
- Adebajo A, Davis P, eds. Rheumatic diseases in African blacks. Seminars in arthritis and rheumatism. Elsevier; 1994. - PubMed
-
- Mijiyawa M. Epidemiology and semiology of rheumatoid arthritis in Third World countries. Revue du rhumatisme (English ed). 1995;62(2):121‐126. - PubMed
-
- Goltzman D, Mannstadt M, Marcocci C. Physiology of the calcium‐parathyroid hormone‐vitamin D axis. Front Horm Res. 2018;50:1‐13. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

