Comprehensive comparison of stroke risk score performance: a systematic review and meta-analysis among 6 267 728 patients with atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 35894866
- PMCID: PMC9681133
- DOI: 10.1093/europace/euac096
Comprehensive comparison of stroke risk score performance: a systematic review and meta-analysis among 6 267 728 patients with atrial fibrillation
Abstract
Aims: Multiple risk scores to predict ischaemic stroke (IS) in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) have been developed. This study aims to systematically review these scores, their validations and updates, assess their methodological quality, and calculate pooled estimates of the predictive performance.
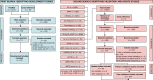
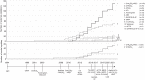
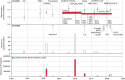
Methods and results: We searched PubMed and Web of Science for studies developing, validating, or updating risk scores for IS in AF patients. Methodological quality was assessed using the Prediction model Risk Of Bias ASsessment Tool (PROBAST). To assess discrimination, pooled c-statistics were calculated using random-effects meta-analysis. We identified 19 scores, which were validated and updated once or more in 70 and 40 studies, respectively, including 329 validations and 76 updates-nearly all on the CHA2DS2-VASc and CHADS2. Pooled c-statistics were calculated among 6 267 728 patients and 359 373 events of IS. For the CHA2DS2-VASc and CHADS2, pooled c-statistics were 0.644 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.635-0.653] and 0.658 (0.644-0.672), respectively. Better discriminatory abilities were found in the newer risk scores, with the modified-CHADS2 demonstrating the best discrimination [c-statistic 0.715 (0.674-0.754)]. Updates were found for the CHA2DS2-VASc and CHADS2 only, showing improved discrimination. Calibration was reasonable but available for only 17 studies. The PROBAST indicated a risk of methodological bias in all studies.
Conclusion: Nineteen risk scores and 76 updates are available to predict IS in patients with AF. The guideline-endorsed CHA2DS2-VASc shows inferior discriminative abilities compared with newer scores. Additional external validations and data on calibration are required before considering the newer scores in clinical practice.
Clinical trial registration: ID CRD4202161247 (PROSPERO).
Keywords: C-statistic; Atrial fibrillation; CHA2DS2-VASc; CHADS2; Calibration; Discrimination; External validation; Ischaemic stroke; Meta-analysis; Prediction model; Predictive performance; Risk score; PROBAST.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Kannel WB, Wolf PA, Benjamin EJ, Levy D. Prevalence, incidence, prognosis, and predisposing conditions for atrial fibrillation: population-based estimates. Am J Cardiol 1998;82:2N–9N. - PubMed
-
- Hart RG, Pearce LA, Aguilar MI. Meta-analysis: antithrombotic therapy to prevent stroke in patients who have nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Ann Intern Med 2007;146:857–67. - PubMed
-
- Lip G, Freedman B, De Caterina R, Potpara TS. Stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation: past, present and future. Comparing the guidelines and practical decision-making. Thromb Haemost 2017;117:1230–9. - PubMed
-
- Wilson PW, D'Agostino RB, Levy D, Belanger AM, Silbershatz H, Kannel WB. Prediction of coronary heart disease using risk factor categories. Circulation 1998;97:1837–47. - PubMed
-
- Hindricks G, Potpara T, Dagres N, Arbelo E, Bax JJ, Blomström-Lundqvist C, et al. . 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur Heart J 2021;42:373–498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

