Ex vivo evaluation of the Ozaki procedure in comparison with the native aortic valve and prosthetic valves
- PMID: 35895002
- PMCID: PMC9443990
- DOI: 10.1093/icvts/ivac199
Ex vivo evaluation of the Ozaki procedure in comparison with the native aortic valve and prosthetic valves
Abstract
Objectives: We investigated the hydrodynamic performance and cusp kinematics of the Ozaki neocuspidized aortic valve in comparison with the native aortic and prosthetic valves in an ex vivo study.
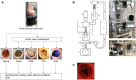
Methods: Native aortic valves of swine hearts were replaced by aortic valve substitutes, and their hydrodynamic performance (effective orifice area and mean pressure gradient) was evaluated in a mock circulation under defined conditions. The following aortic valve substitutes were investigated: native aortic valve, Ozaki valve, Perimount Magna Ease, Trifecta and St. Jude Medical Masters. All prosthetic valves had a labelled size of 21 mm.
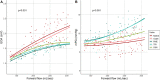
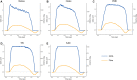
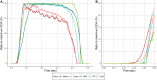
Results: The Ozaki valve and native aortic valve showed a similar and significantly larger orifice area than all investigated prosthetic valves particularly at high flow rates. There was no significant difference between the Ozaki valve and the native aortic valve. The native aortic valve and Ozaki valve showed a similar increase in orifice area with increasing flow through the valve while prosthetic valves showed a markedly weaker increase. Similarly, the native and Ozaki valve showed a similar increase in mPG with forward flow which was weaker than prosthetic valves. Cusp kinematics were similar between the native and Ozaki valve, whilst prosthetic valves were clearly distinguishable from them.
Conclusions: The Ozaki procedure showed excellent hydrodynamic performance compared to prosthetic valves and showed similar cusp motion characteristics to the native aortic valve. Our results suggest that the Ozaki neocuspidized valve behaves physiologically in many aspects, which may contribute to beneficial clinical outcomes.
Keywords: Aortic valve replacement; Ex vivo; Hydrodynamic performance; Ozaki procedure; Valve motion.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Ozaki procedure-re-construction of aortic valve leaflets using autologous pericardial tissue: a review.Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2023 Dec;39(Suppl 2):260-269. doi: 10.1007/s12055-023-01635-z. Epub 2023 Dec 2. Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2023. PMID: 38093925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trifecta versus Perimount Magna Ease aortic valves: Failure mechanisms.Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. 2022 Sep;30(7):797-806. doi: 10.1177/02184923221100994. Epub 2022 May 22. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. 2022. PMID: 35603636 Free PMC article.
-
An ex vivo evaluation of two different suture techniques for the Ozaki aortic neocuspidization procedure.Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2021 Oct 4;33(4):518-524. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivab138. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2021. PMID: 34089604 Free PMC article.
-
Aortic Valve Reconstruction With Autologous Pericardium Versus a Bioprosthesis: The Ozaki Procedure in Perspective.J Am Heart Assoc. 2023 Jan 17;12(2):e027391. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.122.027391. Epub 2023 Jan 11. J Am Heart Assoc. 2023. PMID: 36628965 Free PMC article.
-
Stentless aortic valve replacement: an update.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2011;7:345-51. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S11253. Epub 2011 Jun 2. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2011. PMID: 21731886 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Algorithmic Generation of Parameterized Geometric Models of the Aortic Valve and Left Ventricle.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Dec 24;25(1):11. doi: 10.3390/s25010011. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39796802 Free PMC article.
-
Outcomes of Ozaki Procedure/Aortic Valve Neocuspidization for Aortic Valve Diseases: A Systematic Review.Anatol J Cardiol. 2023 Nov;27(11):619-627. doi: 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2023.3477. Anatol J Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37909351 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Fluid-Structure Interaction Mechanisms for a Native Aortic Valve, Patient-Specific Ozaki Procedure, and a Bioprosthetic Valve.Ann Biomed Eng. 2024 Nov;52(11):3021-3036. doi: 10.1007/s10439-024-03566-1. Epub 2024 Sep 3. Ann Biomed Eng. 2024. PMID: 39225853
-
Comprehensive assessment of aortic flow before and after aortic valve replacement in an ex vivo porcine model with four-dimensional flow magnetic resonance imaging.Interdiscip Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2025 Mar 29;40(4):ivaf087. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivaf087. Interdiscip Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2025. PMID: 40205585 Free PMC article.
-
Ozaki procedure-re-construction of aortic valve leaflets using autologous pericardial tissue: a review.Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2023 Dec;39(Suppl 2):260-269. doi: 10.1007/s12055-023-01635-z. Epub 2023 Dec 2. Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2023. PMID: 38093925 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bourguignon T, Bouquiaux-Stablo A-L, Candolfi P, Mirza A, Loardi C, May M-A. et al. Very long-term outcomes of the Carpentier-Edwards Perimount valve in aortic position. Ann Thorac Surg 2015;99:831–7. - PubMed
-
- Falk V, Baumgartner H, Bax JJ, de Bonis M, Hamm C, Holm PJ. et al.; ESC Scientific Document Group. 2017 ESC/EACTS Guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 2017;52:616–64. - PubMed
-
- Johnson S, Stroud MR, Kratz JM, Bradley SM, Crawford FA, Ikonomidis JS.. Thirty-year experience with a bileaflet mechanical valve prosthesis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2019;157:213–22. - PubMed
-
- Otto CM, Nishimura RA, Bonow RO, Carabello BA, Erwin JP, Gentile F et al 2020 ACC/AHA Guideline for the management of patients with valvular heart disease: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2021;143:e72–e227. - PubMed
-
- Aboud A, Charitos EI, Fujita B, Stierle U, Reil J-C, Voth V. et al. Long-term outcomes of patients undergoing the Ross procedure. J Am Coll Cardiol 2021;77:1412–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

