Gender Moderates Results of a Randomized Clinical Trial for the Khanya Intervention for Substance Use and ART Adherence in HIV Care in South Africa
- PMID: 35895150
- PMCID: PMC9550692
- DOI: 10.1007/s10461-022-03765-8
Gender Moderates Results of a Randomized Clinical Trial for the Khanya Intervention for Substance Use and ART Adherence in HIV Care in South Africa
Abstract
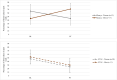
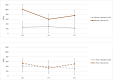
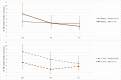
Little is known about gender effects of alcohol and drug use (AOD) among people living with HIV (PLWH) in resource-limited settings. Using multilevel models, we tested whether gender moderated the effect of Khanya, a cognitive-behavioral therapy-based intervention addressing antiretroviral (ART) adherence and AOD reduction. We enrolled 61 participants from HIV care and examined outcomes at 3- and 6-months compared to enhanced treatment as usual (ETAU). Gender significantly moderated the effect of Khanya on ART adherence (measured using electronically-monitored and biomarker-confirmed adherence), such that women in Khanya had significantly lower ART adherence compared to men in Khanya; no gender differences were found for AOD outcomes. Exploratory trajectory analyses showed men in Khanya and both genders in ETAU had significant reductions in at least one AOD outcome; women in Khanya did not. More research is needed to understand whether a gender lens can support behavioral interventions for PLWH with AOD.Trial registry ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03529409. Trial registered on May 18, 2018.
Keywords: ART adherence; Behavioral intervention; Gender differences; South Africa; Substance use.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Safren receives royalties for books on cognitive behavioral therapy from Oxford University Press, Guilford Publications, and Springer/Humana Press. The other authors declare they have no competing interests to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increases in employment over six months following Khanya: A secondary analysis of a pilot randomized controlled trial of a peer-delivered behavioral intervention for substance use and HIV medication adherence in Cape Town, South Africa.Int J Drug Policy. 2024 Dec;134:104632. doi: 10.1016/j.drugpo.2024.104632. Epub 2024 Nov 21. Int J Drug Policy. 2024. PMID: 39577326 Clinical Trial.
-
Project Khanya: results from a pilot randomized type 1 hybrid effectiveness-implementation trial of a peer-delivered behavioural intervention for ART adherence and substance use in HIV care in South Africa.J Int AIDS Soc. 2021 Jun;24 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):e25720. doi: 10.1002/jia2.25720. J Int AIDS Soc. 2021. PMID: 34164935 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Project Khanya: a randomized, hybrid effectiveness-implementation trial of a peer-delivered behavioral intervention for ART adherence and substance use in Cape Town, South Africa.Implement Sci Commun. 2020;1:23. doi: 10.1186/s43058-020-00004-w. Epub 2020 Mar 4. Implement Sci Commun. 2020. PMID: 32607502 Free PMC article.
-
An implementation science protocol of the Women's Health CoOp in healthcare settings in Cape Town, South Africa: A stepped-wedge design.BMC Womens Health. 2017 Sep 18;17(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s12905-017-0433-8. BMC Womens Health. 2017. PMID: 28923034 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol Use and Antiretroviral Therapy Non-Adherence Among Adults Living with HIV/AIDS in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.AIDS Behav. 2020 Jun;24(6):1727-1742. doi: 10.1007/s10461-019-02716-0. AIDS Behav. 2020. PMID: 31673913 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Increases in employment over six months following Khanya: A secondary analysis of a pilot randomized controlled trial of a peer-delivered behavioral intervention for substance use and HIV medication adherence in Cape Town, South Africa.Int J Drug Policy. 2024 Dec;134:104632. doi: 10.1016/j.drugpo.2024.104632. Epub 2024 Nov 21. Int J Drug Policy. 2024. PMID: 39577326 Clinical Trial.
-
Barriers to ART adherence in sub-Saharan Africa: a scoping review toward achieving UNAIDS 95-95-95 targets.Front Public Health. 2025 Jun 10;13:1609743. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1609743. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40556913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Simbayi LC, Zuma K, Zungu N, Moyo S, Marinda E, Jooste S, et al. South African national HIV prevalence, incidence, behaviour and communication survey, 2017. Cape Town: HSRC Press; 2019.