Ribosomal RNA-Depletion Provides an Efficient Method for Successful Dual RNA-Seq Expression Profiling of a Marine Sponge Holobiont
- PMID: 35895230
- PMCID: PMC9385839
- DOI: 10.1007/s10126-022-10138-8
Ribosomal RNA-Depletion Provides an Efficient Method for Successful Dual RNA-Seq Expression Profiling of a Marine Sponge Holobiont
Abstract
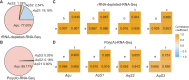
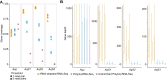
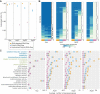
Investigations of host-symbiont interactions can benefit enormously from a complete and reliable holobiont gene expression profiling. The most efficient way to acquire holobiont transcriptomes is to perform RNA-Seq on both host and symbionts simultaneously. However, optimal methods for capturing both host and symbiont mRNAs are still under development, particularly when the host is a eukaryote and the symbionts are bacteria or archaea. Traditionally, poly(A)-enriched libraries have been used to capture eukaryotic mRNA, but the ability of this method to adequately capture bacterial mRNAs is unclear because of the short half-life of the bacterial transcripts. Here, we address this gap in knowledge with the aim of helping others to choose an appropriate RNA-Seq approach for analysis of animal host-bacterial symbiont transcriptomes. Specifically, we compared transcriptome bias, depth and coverage achieved by two different mRNA capture and sequencing strategies applied to the marine demosponge Amphimedon queenslandica holobiont. Annotated genomes of the sponge host and the three most abundant bacterial symbionts, which can comprise up to 95% of the adult microbiome, are available. Importantly, this allows for transcriptomes to be accurately mapped to these genomes, and thus quantitatively assessed and compared. The two strategies that we compare here are (i) poly(A) captured mRNA-Seq (Poly(A)-RNA-Seq) and (ii) ribosomal RNA depleted RNA-Seq (rRNA-depleted-RNA-Seq). For the host sponge, we find no significant difference in transcriptomes generated by the two different mRNA capture methods. However, for the symbiont transcriptomes, we confirm the expectation that the rRNA-depleted-RNA-Seq performs much better than the Poly(A)-RNA-Seq. This comparison demonstrates that RNA-Seq by ribosomal RNA depletion is an effective and reliable method to simultaneously capture gene expression in host and symbionts and thus to analyse holobiont transcriptomes.
Keywords: Demosponge; Holobiont; Hologenome; Porifera; Transcriptomics.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Potential for host-symbiont communication via neurotransmitters and neuromodulators in an aneural animal, the marine sponge Amphimedon queenslandica.Front Neural Circuits. 2023 Sep 29;17:1250694. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2023.1250694. eCollection 2023. Front Neural Circuits. 2023. PMID: 37841893 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of RNA-Seq by poly (A) capture, ribosomal RNA depletion, and DNA microarray for expression profiling.BMC Genomics. 2014 Jun 2;15(1):419. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-419. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24888378 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal dynamics of prokaryotic communities in the marine sponge Sarcotragus spinosulus.Mol Ecol. 2014 Jun;23(12):3097-112. doi: 10.1111/mec.12789. Epub 2014 Jun 9. Mol Ecol. 2014. PMID: 24814756
-
The Sponge Hologenome.mBio. 2016 Apr 21;7(2):e00135-16. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00135-16. mBio. 2016. PMID: 27103626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic insights into the marine sponge microbiome.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012 Sep;10(9):641-54. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2839. Epub 2012 Jul 30. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22842661 Review.
Cited by
-
Cefazolin shifts the kidney microbiota to promote a lithogenic environment.Nat Commun. 2024 Dec 11;15(1):10509. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-54432-6. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39663374 Free PMC article.
-
Potential for host-symbiont communication via neurotransmitters and neuromodulators in an aneural animal, the marine sponge Amphimedon queenslandica.Front Neural Circuits. 2023 Sep 29;17:1250694. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2023.1250694. eCollection 2023. Front Neural Circuits. 2023. PMID: 37841893 Free PMC article.
-
Dual RNA-seq in filarial nematodes and Wolbachia endosymbionts using RNase H based ribosomal RNA depletion.Front Microbiol. 2024 May 20;15:1418032. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1418032. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38832111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G. Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet. 2000;25:25–29. doi: 10.1038/75556. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baddal B, Muzzi A, Censini S, Calogero RA, Torricelli G, Guidotti S, Taddei AR, Covacci A, Pizza M, Rappuoli R, Soriani M, Pezzicoli A. Dual RNA-seq of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae and host cell transcriptomes reveals novel insights into host-pathogen cross talk. mBio 6:e01765–15. 2015;6:e01765–15. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01765-15. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
