Combined Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2: Rapid Antigen Detection as an Adjunct to Nucleic Acid Detection
- PMID: 35895307
- PMCID: PMC9384589
- DOI: 10.1093/labmed/lmac089
Combined Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2: Rapid Antigen Detection as an Adjunct to Nucleic Acid Detection
Abstract
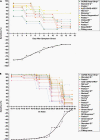
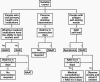
Coronavirus disease 2019 is a serious threat to human life, and early diagnosis and screening can help control the COVID-19 pandemic. The high sensitivity of reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assay is the gold standard for the diagnosis of COVID-19, but there are still some false-negative results. Rapid antigen detection (RAD) is recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a screening method for COVID-19. This review analyzed the characteristics of RDT and found that although the overall sensitivity of RAD was not as high as that of RT-PCR, but RAD was more sensitive in COVID-19 patients within 5 days of the onset of symptoms and in COVID-19 patients with Ct ≤ 25. Therefore, RAD can be used as an adjunct to RT-PCR for screening patients with early COVID-19. Finally, this review provides a combined diagnostic protocol for RAD and nucleic acid testing with the aim of providing a feasible approach for COVID-19 screening.
Keywords: COVID-19; Early screening; Lateral flow immunoassay; RT-PCR; Sensitivity.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pathology. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO): Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak situation. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019. Accessed March 13, 2022.
-
- World Health Organization (WHO): Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Pandemic — Emergency Use Listing Procedure (EUL) Open for IVDs. https://extranet.who.int/pqweb/vitro-diagnostics/coronavirus-disease-cov.... Accessed March 13, 2022.
-
- US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim Guidance for Rapid Antigen Testing for SARS-CoV-2. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/lab/resources/antigen-tests-gu.... Accessed March 13, 2022.
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Options for the Use of Rapid Antigen Tests for COVID-19 in the EU/EEA and the UK. (https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/publications-data/options-use-rapid-antige...). Accessed 13 March 2022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

