Apelin Association with Hepatic Fibrosis and Esophageal Varices in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Virus
- PMID: 35895373
- PMCID: PMC9294707
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.21-0085
Apelin Association with Hepatic Fibrosis and Esophageal Varices in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C Virus
Abstract
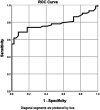
Portal hypertension and esophageal varices complicating hepatitis C virus (HCV)-related chronic liver diseases are some of the most devastating sequelae. Angiogenesis is the hallmark of their pathogenesis. Apelin is one of the recently identified angiogenic and fibrogenic peptides. We studied apelin gene expression, apelin (rs3761581) single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), and serum apelin level in patients with chronic HCV, and their association with liver fibrosis and esophageal varices in 112 patients with HCV-related chronic liver disease (40 with liver cirrhosis [LC]/low-grade varices, 33 with LC/high-grade varices, and 39 with fibrotic non-cirrhotic liver/no varices) and 80 healthy control subjects. Real-time polymerase chain reaction was used for apelin gene expression assay and apelin rs3761581 SNP analysis in peripheral blood samples. The serum apelin level was measured by ELISA. Apelin gene expression was undetectable in the studied samples. The SNP analysis revealed a greater frequency of the C (mutant) allele among patients compared with control subjects (P = 0.012; odds ratio, 3.67). The serum apelin level was significantly greater in patients with LC/varices (median, 31.6 ng/L) compared with patients without LC/varices (median, 2.9 ng/L; P < 0.001). A serum apelin level cutoff value of 16.55 ng/L predicted the presence of varices, with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve value of 0.786. A positive correlation was found between serum apelin level and grade of liver fibrosis (r = 0.346, P < 0.001) and portal hypertension (r = 0.438, P < 0.001). In conclusion, the apelin rs3761581-C allele may be associated with the progression of HCV-related chronic liver disease and varices formation, and can be considered a potential therapeutic target to control fibrosis progression. The serum apelin level provided an accurate prediction of the presence of esophageal varices.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Can transient elastography, Fib-4, Forns Index, and Lok Score predict esophageal varices in HCV-related cirrhotic patients?Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014 Feb;37(2):58-65. doi: 10.1016/j.gastrohep.2013.09.008. Epub 2013 Dec 21. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24365388 Clinical Trial.
-
Study of the influence of heme oxygenase 1 gene single nucleotide polymorphism (rs2071746) on esophageal varices among patients with cirrhosis.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Aug;30(8):888-892. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001161. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 29877949
-
Correlations of portal hypertensive gastropathy of hepatitis B cirrhosis with other factors.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2002 Nov;1(4):527-31. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2002. PMID: 14607680
-
Managing liver cirrhotic complications: Overview of esophageal and gastric varices.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2020 Oct;26(4):444-460. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2020.0022. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 33053928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation and treatment of esophageal varices in the cirrhotic patient.Isr Med Assoc J. 2013 Feb;15(2):109-15. Isr Med Assoc J. 2013. PMID: 23516775 Review.
References
-
- Berzigotti A Seijo S Reverter E Bosch J , 2013. Assessing portal hypertension in liver diseases. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 7: 141–155. - PubMed
-
- Zayed RA Omran D Zayed AA Elmessery LO , 2017. Determinants of infection outcome in HCV-genotype 4. Viral Immunol 8: 560–567. - PubMed
-
- Garcia‐Tsao G Sanyal AJ Grace ND Carey W , 2007. Prevention and management of gastroesophageal varices and variceal hemorrhage in cirrhosis. Hepatology 46: 922–938. - PubMed
-
- D’amico G Pagliaro L Bosch J , 1999. Pharmacological treatment of portal hypertension: an evidence-based approach. Semin Liver Dis 19: 475–505. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

