A quantification method of somatic mutations in normal tissues and their accumulation in pediatric patients with chemotherapy
- PMID: 35895679
- PMCID: PMC9351471
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2123241119
A quantification method of somatic mutations in normal tissues and their accumulation in pediatric patients with chemotherapy
Abstract
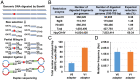
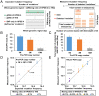
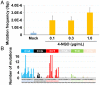
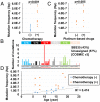
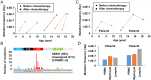
Somatic mutations are accumulated in normal human tissues with aging and exposure to carcinogens. If we can accurately count any passenger mutations in any single DNA molecule, since their quantity is much larger than driver mutations, we can sensitively detect mutation accumulation in polyclonal normal tissues. Duplex sequencing, which tags both DNA strands in one DNA molecule, enables accurate count of such mutations, but requires a very large number of sequencing reads for each single sample of human-genome size. Here, we reduced the genome size to 1/90 using the BamHI restriction enzyme and established a cost-effective pipeline. The enzymatically cleaved and optimal sequencing (EcoSeq) method was able to count somatic mutations in a single DNA molecule with a sensitivity of as low as 3 × 10-8 per base pair (bp), as assessed by measuring artificially prepared mutations. Taking advantages of EcoSeq, we analyzed normal peripheral blood cells of pediatric sarcoma patients who received chemotherapy (n = 10) and those who did not (n = 10). The former had a mutation frequency of 31.2 ± 13.4 × 10-8 per base pair while the latter had 9.0 ± 4.5 × 10-8 per base pair (P < 0.001). The increase in mutation frequency was confirmed by analysis of the same patients before and after chemotherapy, and increased mutation frequencies persisted 46 to 64 mo after chemotherapy, indicating that the mutation accumulation constitutes a risk of secondary leukemia. EcoSeq has the potential to reveal accumulation of somatic mutations and exposure to environmental factors in any DNA samples and will contribute to cancer risk estimation.
Keywords: chemotherapy; duplex sequencing; next-generation sequencing; normal tissue; somatic mutation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ushijima T., Clark S. J., Tan P., Mapping genomic and epigenomic evolution in cancer ecosystems. Science 373, 1474–1479 (2021). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

