CMOS electrochemical pH localizer-imager
- PMID: 35895813
- PMCID: PMC9328676
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abm6815
CMOS electrochemical pH localizer-imager
Abstract
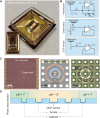
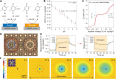
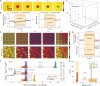
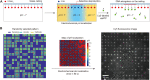
pH controls a large repertoire of chemical and biochemical processes in water. Densely arrayed pH microenvironments would parallelize these processes, enabling their high-throughput studies and applications. However, pH localization, let alone its arrayed realization, remains challenging because of fast diffusion of protons in water. Here, we demonstrate arrayed localizations of picoliter-scale aqueous acids, using a 256-electrochemical cell array defined on and operated by a complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS)-integrated circuit. Each cell, comprising a concentric pair of cathode and anode with their current injections controlled with a sub-nanoampere resolution by the CMOS electronics, creates a local pH environment, or a pH "voxel," via confined electrochemistry. The system also monitors the spatiotemporal pH profile across the array in real time for precision pH control. We highlight the utility of this CMOS pH localizer-imager for high-throughput tasks by parallelizing pH-gated molecular state encoding and pH-regulated enzymatic DNA elongation at any selected set of cells.
Figures

References
-
- Thomas P. G., Russell A. J., Fersht A. R., Tailoring the pH dependence of enzyme catalysis using protein engineering. Nature 318, 375–376 (1985).
-
- Ludwig M.-G., Vanek M., Guerini D., Gasser J. A., Jones C. E., Junker U., Hofstetter H., Wolf R. M., Seuwen K., Proton-sensing G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature 425, 93–98 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Bullough P. A., Hughson F. M., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C., Structure of influenza haemagglutinin at the pH of membrane fusion. Nature 371, 37–43 (1994). - PubMed
-
- Stegmann T., Booy F. P., Wilschut J., Effects of low pH on influenza virus. Activation and inactivation of the membrane fusion capacity of the hemagglutinin. J. Biol. Chem. 262, 17744–17749 (1987). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

