The Gab2-MALT1 axis regulates thromboinflammation and deep vein thrombosis
- PMID: 35895897
- PMCID: PMC9523376
- DOI: 10.1182/blood.2022016424
The Gab2-MALT1 axis regulates thromboinflammation and deep vein thrombosis
Abstract
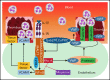
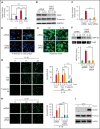
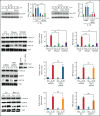
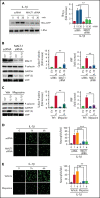
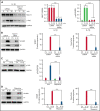
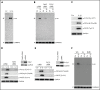
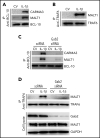
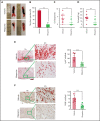
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is the third most common cause of cardiovascular mortality. Several studies suggest that DVT occurs at the intersection of dysregulated inflammation and coagulation upon activation of inflammasome and secretion of interleukin 1β (IL-1β) in restricted venous flow conditions. Our recent studies showed a signaling adapter protein, Gab2 (Grb2-associated binder 2), plays a crucial role in propagating inflammatory signaling triggered by IL-1β and other inflammatory mediators in endothelial cells. The present study shows that Gab2 facilitates the assembly of the CBM (CARMA3 [CARD recruited membrane-associated guanylate kinase protein 3]-BCL-10 [B-cell lymphoma 10]-MALT1 [mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1]) signalosome, which mediates the activation of Rho and NF-κB in endothelial cells. Gene silencing of Gab2 or MALT1, the effector signaling molecule in the CBM signalosome, or pharmacological inhibition of MALT1 with a specific inhibitor, mepazine, significantly reduced IL-1β-induced Rho-dependent exocytosis of P-selectin and von Willebrand factor (VWF) and the subsequent adhesion of neutrophils to endothelial cells. MALT1 inhibition also reduced IL-1β-induced NF-κB-dependent expression of tissue factor and vascular cell adhesion molecule 1. Consistent with the in vitro data, Gab2 deficiency or pharmacological inhibition of MALT1 suppressed the accumulation of monocytes and neutrophils at the injury site and attenuated venous thrombosis induced by the inferior vena cava ligation-induced stenosis or stasis in mice. Overall, our data reveal a previously unrecognized role of the Gab2-MALT1 axis in thromboinflammation. Targeting the Gab2-MALT1 axis with MALT1 inhibitors may become an effective strategy to treat DVT by suppressing thromboinflammation without inducing bleeding complications.
© 2022 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Endothelial cell-mediated venous thrombosis.Blood. 2022 Sep 29;140(13):1459-1460. doi: 10.1182/blood.2022017938. Blood. 2022. PMID: 36173663 No abstract available.
-
What the neighbors say.J Thromb Haemost. 2022 Dec;20(12):2721. doi: 10.1111/jth.15904. J Thromb Haemost. 2022. PMID: 36372446 No abstract available.
References
-
- Klemen ND, Feingold PL, Hashimoto B, et al. . Mortality risk associated with venous thromboembolism: a systematic review and Bayesian meta-analysis. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7(8):e583-e593. - PubMed
-
- Søgaard KK, Schmidt M, Pedersen L, Horváth-Puhó E, Sørensen HT. 30-year mortality after venous thromboembolism: a population-based cohort study. Circulation. 2014;130(10):829-836. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

