'Difficult to treat' rheumatoid arthritis: current position and considerations for next steps
- PMID: 35896282
- PMCID: PMC9335059
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002387
'Difficult to treat' rheumatoid arthritis: current position and considerations for next steps
Abstract
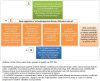
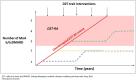
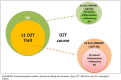
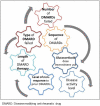
The European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology recently defined difficult to treat (D2T) rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and provided points to consider in its management. This review summarises the key concepts of D2T-RA that underpinned this recent guidance. D2T-RA is primarily characterised by failure of at least two different mechanism of action biologic/targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARDs) with evidence of active/progressive disease. The basis for progressive disease, however, is not limited to clear inflammatory joint pathology, capturing wider contributors to treatment cycling such as comorbidity, obesity and fibromyalgia. This means D2T-RA comprises a heterogeneous population, with a proportion within this exhibiting bona fide treatment-refractory disease. The management points to consider, however, emphasise the importance of checking for the presence of inflammatory pathology before further treatment change. This review suggests additional considerations in the definition of D2T-RA, the potential value in identifying D2T traits and intervening before the development of D2T-RA state and the need for real world evidence of targeted synthetic DMARD in this population to compare to recent trial data. Finally, the review asks whether the presence of D2T-RA implies a failure to treat effectively from the outset, and the need for pharmacological and non-pharmacological management approaches to address the wider D2T-RA population effectively.
Keywords: biological therapy; rheumatoid arthritis; therapeutics.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: MHB is supported by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) Manchester Biomedical Research Centre and is in receipt of an NIHR Senior Investigator award.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
