Elite Adolescent Ice Hockey Players: Analyzing Associations between Anthropometry, Fitness, and On-Ice Performance
- PMID: 35897327
- PMCID: PMC9330307
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph19158952
Elite Adolescent Ice Hockey Players: Analyzing Associations between Anthropometry, Fitness, and On-Ice Performance
Abstract
In the field of ice hockey, body mass and height have always played a role in team selection. This study aims to analyze the associations between anthropometry and multiple dimensions of performance among elite adolescent ice hockey players.
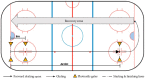
Methods: 187 adolescent players (males: n = 80, 13.81 years; females: n = 107, 14.96 years) took part in the study, in Camp 1. Off-ice fitness and on-ice skating tests were performed. Camp 2 consists of on-ice tests and match performance with players selected by coaching staff at Camp 1. Camp 2 data came from official matches performance and a combination of skating tests and intrasquad matches. Hockey Quebec's selection process consists of going from an entire pool of athletes to a team of twenty-five players, through several camps spread over two years. Correlation analyses were conducted to verify associations between anthropometric measures and performances.
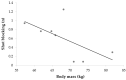
Results: In Camp 1, heavier-taller male athletes displayed better performances in most off-ice fitness tests, while heavier female athletes tended to display poorer performance. Camp 2 showed no significant correlations in on-ice tests and match performance. However, some tendencies were observed: heavier male players were less involved in blocked shots, and taller females were more agile.
Conclusions: Despite off-ice advantages, the taller-heavier prototype does not translate directly to better performance on the ice among elite adolescent players. Coaches should analyze anthropometric characteristics with caution, and place more focus on match-specific abilities to identify talent.
Keywords: body mass; fitness assessment; height; match performance; on-ice testing; selection camps; talent identification; young athletes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Vigh-Larsen J.F., Ermidis G., Rago V., Randers M.B., Fransson D., Nielsen J.L., Gliemann L., Piil J.F., Morris N.B., de Paoli F.V., et al. Muscle Metabolism and Fatigue during Simulated Ice Hockey Match-Play in Elite Players. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2020;52:2162–2171. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000002370. - DOI - PubMed
-
- International Ice Hockey Federation Survey of Players. [(accessed on 14 May 2022)]. Available online: https://www.iihf.com/en/static/5324/survey-of-players.
-
- PubMed Ice Hockey Research Publications. [(accessed on 14 May 2022)]; Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=ice+hockey.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

